MS Exchange Backup
When Amanda is configured and licensed for MS Exchange backup, Amanda uses the Microsoft Windows Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to back up the Exchange database and logs. ZWC backs up and restores MS Exchange at Storage Group level. However, ZWC supports restoring individual stores as well.
Requirements for MS Exchange Backup
These instructions assume you have already installed and licensed the Amanda server and the MS Exchange server being backed up. Because the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) takes care of any necessary file locking and transaction log pruning during the backup process, the requirements are simple:
- The following MS Exchange versions are supported on Windows 2003 Server (Service Pack 2 or later) editions:
- Exchange 2003 (32 bit)
- Exchange 2007 (32 & 64 bit)
- Run the command vssadmin list writers at the Windows command prompt and check that the state of the Exchange Writer is stable. If not (or if there are any VSS errors), restart the Volume Shadow Copy Service.
In case of Windows 2003 Small Business Server edition, the Exchange Writer is disabled by default. Please follow the instructions this MS knowledgebase article to enable the Exchange Writer: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/838183
- Make sure that the Exchange Storage Groups are in Mounted state.
- Exchange circular logging must be disabled. If circular logging is enabled, the Exchange server client will only retain the last 5 transaction logs, which may not be sufficient to restore to the most recent backup.
- The Zmanda Windows Client must be installed on the Exchange server as described here.
Configuring MS Exchange Backups
The Zmanda Client for Windows uses snapshots for Exchange server backups. The procedure described below only backs up the Exchange database and related data files. Other files (such as the Exchange installation directory) require separate configuration for backup.
Creating a Backup Set for Exchange Servers in the ZMC
Create a dedicated backup set for each MS Exchange server you intend to back up. On the Backup What page you are prompted to select what type of object you want to back up. Choose MS Exchange, and the following options are displayed:
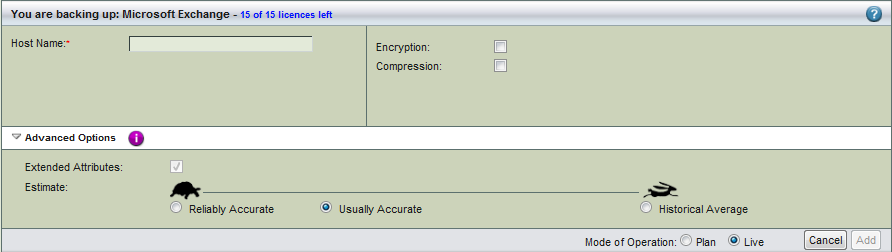
- Host Name
- The name or IP address of the machine running the MS Exchange server you intend to back up.
- Encryption
- Check the box to enable server-side encryption of the backup images.
- Compression
- Check the box to compress backup images before transfer to the Amanda backup server.
- Advanced Options
- Extended attributes are always backed up on Windows clients regardless of application. For details on the Estimate option, see the Backup Where Advanced Options help.
After you have set the options, click Add to Table to add the MS Exchange object to the backup set. Click Apply to Server to commit the changes; you can then configure the backup set just as you would any other by setting the options on Backup Where, Backup How, and Backup When, etc.
Important note: ZWC supports Full and Differential backup method of Exchange. During a Level 0 (Full) backup, ZWC backs up all databases, transaction logs and checkpoint file. After a level 0 backup, the Exchange Writer automatically truncates the committed logs. For backup levels greater than 0, ZWC will do a Differential backup in which only the transaction logs will be backed up. No logs will be truncated after a differential backup.
Protecting all the MS Exchange Components
Servers running Exchange Server 2003 and 2007 use Active Directory extensively for the following:
- Active Directory is the configuration repository for Exchange organization data. Without this configuration information, Exchange servers cannot start or function.
- All Exchange directory information is stored in Active Directory. This includes configuration information for all mailboxes, contacts, distribution lists, servers, and sites within the Exchange organization.
- Items such as distribution lists and access permissions for users and groups are also stored within Active Directory
Because Exchange depends so heavily on Active Directory, it is crucial to back up the System State of an Exchange Server along with System State of the Domain Controller running in the Exchange environment so that the Exchange configuration stored in the Active Directory also gets backed up.
Zmanda recommends that you configure separate backup sets for Exchange and System State backups.
Configuring MS Exchange Restores from the Zmanda Management Console
In the event of a server loss, how you perform the recovery will depend on the server role and your disaster recovery plan. Server loss can be caused by software or hardware failure, or by the physical loss of the site where the server was housed. One would also need to recover Exchange databases in case of issues such as database corruption, loss of transaction logs, accidental deletion of mailboxes, etc. Exchange databases can be restored to the same server or to an alternate server depending on the Disaster Recovery plan decided by the Exchange Administrator.
3 types of recovery operations are allowed by Microsoft Exchange:
- roll-forward,
- point in time
- full restore
The state of the MS Exchange server when the restore is started determines what type of recovery will be available. Please see this Microsoft documentation for details on Exchange recoveries.
Here are the steps to follow to restore and recover Exchange using ZWC to the original server or a different server.
Restoring to the Original Server:
In case of Exchange database corruption or loss of the transaction log, you would want to restore the backed up data to the original server. Before restoring the data, make sure that MS Exchange is installed on the server and that the entire storage group containing the databases to be restored is in the Dismounted state. If restoring individual databases (which is only possible if circular logging was disabled during the backup), circular logging must be disabled for the restore.
Also make sure that the This database can be overwritten by restore option is selected from the Exchange System Manager (Exchange 2003) or Exchange Management Console (Exchange 2007). The Zmanda Windows Client automatically stops the Microsoft Exchange Information Store service as a pre-restore operation and will start it again once the restore is complete.
- Open Zmanda Management Console and go to the Restore What page.
- Enter the original Exchange Server details in the Initial Host field. If the backup set contains a single DLE for Exchange, msexchange is pre-entered in the Initial Directory field. If the backup set contains more than one DLE, select msexchange from the list. Click Explore to view the data. Select the data to be restored and then click Next.
- On the Restore->Where page, enter the details of the destination Exchange Server in the Destination Host field. Select Windows as the Destination Host Type. Enter the Destination Username if it is something other than amandabackup. Leave the Destination directory blank if restoring data to the original location. To restore the data to an alternative location, see the next section.
- Specify a Temporary Directory to change the default location of /tmp if desired, then click Next.
- Review the Restore From and Restore To settings on the Restore->Restore page. Once confirmed, click Restore to start the restore process.
Important Note: After the Exchange data has been restored, ZWC automatically starts the Microsoft Exchange Information Store service. When the storage group is mounted, the Exchange store automatically replays any pending transactions using the Exchange Server soft recovery feature. Therefore all restores performed through the Zmanda Windows Client are always "roll-forward" restores. You must mount the databases that were dismounted for the restore.
Restoring to an Alternate (or Recovery) Server
There are two reasons to restore to a different machine than that from which the backup was taken:
- a disaster has destroyed the original hardware. You must restore the database to a rebuilt Exchange Server or to an alternate Exchange server.
- you are recovering an individual mailbox. In this case, there are additional steps to apply the recovery to the production Exchange server (see the next section below).
There are some pre-requisites to restore to a recover server:
- The target server must have the same Windows OS version and Service Packs as the source server.
- Exchange must be installed and must have the same Organization and Administrative Group name as the source server.
- The storage groups and databases must already exist on the target server, and have the same names as the original storage groups or databases.
- The databases must be in the Dismounted state and the This database can be overwritten by restore option enabled through the Exchange System Manager (Exchange 2003) or Exchange Management Console (Exchange 2007).
- Because you are restoring to an alternate "recovery server" that has a different set of log files, the the signatures on the log files must match. To ensure this, either rename the E0x.log file located in the Transaction log directory, or enable the Do not mount the database option while creating a Mailbox or Public folder store.
Zmanda Client for Windows automatically stops the Microsoft Exchange Information Store service before the restore operation and starts again once the restore operation is complete.
- Open the Zmanda Management Console and go to the Restore Page.
- Enter the original Exchange Server details in the Initial Host field. Select "msexchange" as the "Initial Directory". Click on "Explore" to view the data. Select the data to be restored and click Next.
- On the Restore->Where page, enter the details of the destination Exchange Server in the Destination Host field. Select Windows as the Destination Host Type. Enter the Destination Username if it is something other than amandabackup. To restore the data to an alternate location, enter the appropriate Destination directory.
- Review the options on the Restore->Restore page. Once confirmed, click Restore to start the restore process.
Recovering a Mailbox
To recover a mailbox, restore to a recovery server as described above, then follow these additional steps:
- Using the Exchange System Manager, run the Cleanup Agent on the Mailboxes to display the restored mailboxes. Then Reconnect the mailbox from which you wish to retrieve the mails to its associated User account. For example, if you want to retrieve mails for user Administrator, then reconnect the Administrator mailbox to Administrator user account.
- Use Microsoft's exmerge.exe utility to extract the mails into a PST. Use the Two step procedure, and select Step 1 to create the PST file.
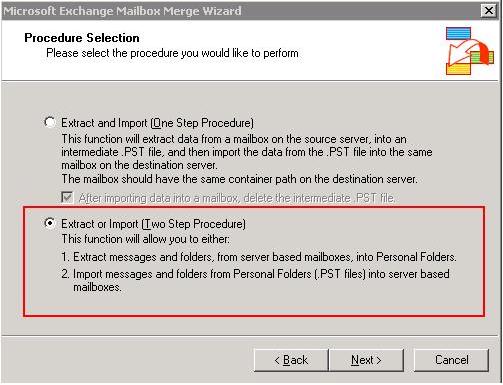
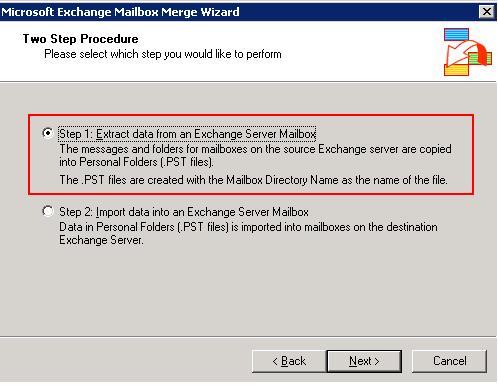
- Copy the PST file to the production server.
- Run the exmerge.exe utility on the production server to merge the PST mails into the required mailbox. Use the Two step procedure, and select Step 2 to Import the data into an Exchange Server Mailbox.
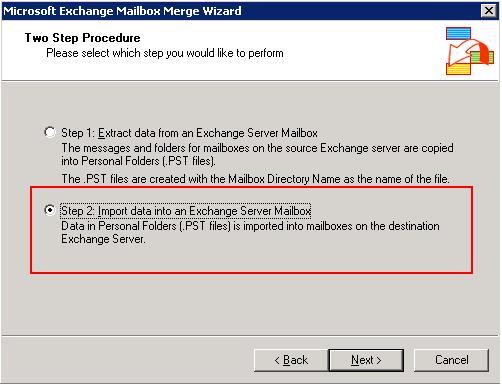
The deleted emails should now be recovered.
Troubleshooting Backups
- If an Exchange backup fails, follow these troubleshooting steps:
-
- Examine the Windows Event Viewer for any VSS or Exchange Writer errors. Run the command vssadmin list writers at the Windows command prompt and check that the state of the Exchange Writer is stable. If not (or if there are any VSS errors, restart the Exchange Writer and Volume Shadow Copy Service.
- Make sure that the Exchange Storage Groups are in Mounted state.
- If a snapshot backup of an Exchange Server 2003 database fails, and event ID 9607 is logged, refer to this Microsoft Knowledgebase article.
- If event ID 9840 or 9607 is logged when a VSS backup operation fails in Exchange 2007 or in Exchange 2003, see this Microsoft Knowledgebase article.
Troubleshooting Restores
- If the Exchange Storage Groups do not mount, refer to Microsoft documentation describing MS exchange storage group access for further information: Top 10 Database Mounting Issues and Their Solutions
- Some important Microsoft documentation for better understanding of Exchange recovery strategies: How to recover or to restore a single mailbox in Exchange Server 2003, and the Exchange 2003 Disaster Recovery Operations Guide
