Table of contents
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Downloading and Installing Zmanda Windows Client
- 1.3. Installation Troubleshooting
- 1.4. Changing the Location of the Installation Data Directory
- 1.5. Backing Up Windows Clients
- 1.6. Restoring a Windows Client
- 1.6.1. Completing the Restore Where page for Windows Clients
- 1.6.1.1. Destination Host Type
- 1.6.1.2. Destination Directory
- 1.6.1. Completing the Restore Where page for Windows Clients
- 1.7. Windows system state backup and recovery
- 1.7.1. Workstations
- 1.7.2. Domain Controllers
- 1.7.3. Windows System State Backup from the ZMC
- 1.7.4. Windows System State Restore from the ZMC
- 1.8. Changing the password for the amandabackup user
- 1.9. Zmanda Windows Client configuration utility
- 1.10. Invoking Pre- and Post-backup Scripts
- 1.11. Compatibility with previous versions of the Zmanda Windows Client
- 2. Running the Windows Client Support Script
- 2.1. Location
- 2.2. Files Gathered
- 2.2.1. Zmanda Windows Client Installation Logs
- 2.2.2. Zmanda Windows Client Debug Logs:
- 2.2.3. System Logs:
- 2.2.4. Additional information:
- 2.3. Output File
Introduction
Zmanda Windows Client (or ZWC) backs up data from Microsoft Windows clients to an Amanda backup server. It is compatible with the following operating system versions:
- Windows XP Pro (Service Pack 2) running on the x86 platform
- Windows 2003 server running on the x86 platform
- Windows Vista running on the x86 platform
Windows clients must open inbound TCP ports 10080 and 10081, and outbound TCP ports 700:800.
Downloading and Installing Zmanda Windows Client
Important Note: During installation, an amandabackup user account is created on the Zmanda Windows Client using local rules (i.e., Domain Controller/Domain/Standalone Workstation) for password creation. These OS users run backup and restore processes. When you change the account passwords eventually, be careful to ensure that security policies (such as strong passwords, password expiration) are followed. If an amandabackup user password expires, the Zmanda Windows Client service will fail to start, returning a Login Failure message.
- Download the Zmanda Windows Client software from the Zmanda network downloads page. Please have your Zmanda network Username and Password ready; you will need them to access the download page. Depending on the licenses you have purchased, the downloads page will let you download one (or more) of the following archive packages:
ZWCInstaller-Desktop-264-32bit.zip
ZWCInstaller-Desktop-264-64bit.zip
ZWCInstaller-Server-264-32bit.zip
ZWCInstaller-Server-264-64bit.zip
The different packages correspond to the different setup programs necessary for 32- and 64-bit server and desktop installation options.
Desktop versions are required for Windows XP and Vista, server versions are required for Windows 2003 and 2008 server. You should install the 32-bit version on 32-bit platforms and the 64-bit version on 64-bit platforms. - Extract the zip file to the appropriate Windows machine and run the Setup.exe program.
- Follow the on-screen instructions. When asked to select an installation directory, you may want to change from the default location (C:\Program Files), as the Zmanda Windows Client internal databases can consume a lot of disk space and also affect the performance of other applications that depend on the same disk when processing backups. You will also need to set a password for the amandabackup user on the Windows client. You will also need to know the Fully Qualified Domain Name or IP address of the Amanda server to which this client will back up. Multiple Amanda servers can be added using comma-separated syntax.
- If there were any problems or errors, refer to the error logs as described in the next section.
Unattended Enterprise Installations
Because the Zmanda Windows Client is packaged as an .msi file, you can use the Windows Installer tool (msiexec.exe) in conjunction with other enterprise deployment and distribution tools (either from Microsoft or other vendors) to perform multiple, unattended installations in a large-scale environment. Enterprise installation tools are described in more detail here.
The msiexec command line to perform an unattended installation of the Zmanda Windows Client is:
- msiexec /package [path\]ZWCInstaller.msi /passive /norestart /l C:\ZWCInst.log
The example above causes the Windows Installer to display a status bar and log any installation messages to C:\ZWCInst.log. To run the Installer without the status bar, use the /quiet option. You can also specify different paths for the ZWCInstaller.msi and log file if desired.
Post-installation steps for Windows Vista
On Windows Vista, the ZWCService service must be manually added to the "Exceptions" list for the Windows Firewall. If the Windows Firewall is ON, the Zmanda Management Console will be unable to communicate with the with Zmand Windows Client service unless you follow these steps after installing the client:
- Open the Windows Firewall from the Administrative Tools->Control Panel.
- Click on the Exceptions tab.
- Click on Add Program,, then browse to the Zmanda Client for Windows install path. Select ZWCService.exe located in the bin directory.
- Click Apply.
Installation Troubleshooting
If the installation failed for some reason, the ZWC installer rolls back the installation to the last working configuration.
The installation program logs messages to the following locations:
- The Windows $temp directory (MSIMM:DD:HH.txt) The MSI-generated files are named by date and time rather than by the software being installed.
- Successful installation messages are logged to C:\Program Files\Zmanda\Zmanda Client for Windows\Debug\LogFile.txt
- Installation failures are logged to C:\zwc_install.log.
Installation can fail for a variety of reasons. For example, the user set a Password not conforming to Windows requirements, or running the installation program without the necessarily permissions. The log messages will explain what went wrong.
Changing the Location of the Installation Data Directory
Depending on the size of backup sets and the number of backup runs scheduled for your organization, the Zmanda Windows Client can consume a lot (>1G) of disk space, and also affect the performance of other applications that depend on the same disk while backups are running. The files that tend to grow are listed below:
- c:\program files\zmanda\zmanda client for windows\MySQL\data is where the catalog file(s) are stored. If you move these files, the new location must be specified in the ZWC my.ini file.
- c:\program files\zmanda\zmanda client for windows\misc is where the backup set header files are stored. This location can be changed using the ZWCConfig utility.
If you find that the ZWC installation is consuming too much disk space while processing backup sets, you can move location of these files. There are two methods of doing this:
- By uninstalling ZWC and re-installing it on a different volume (preferred).
- By manually moving the catalog and backup set header files and editing the my.ini file and Windows Registry to specify the new locations (see the steps listed below).
- Use the Control Panel to stop both the ZWCService and the ZWC-MySQL services.
- Move the data directory under ZWC_Installation_Directory\MySQL\Data to the new location. For example, move C:\Program Files\Zmanda\Zmanda Client for Windows\MySQL\data to F:\MySQL\data
- Open the my.ini located in ZWC_Installation_Directory\MySQL\my.ini and put the following entry under the [mysqld] section:
----------------------------------------------
[mysqld]
datadir=SQL_data_dir
----------------------------------------------
where SQL_data_dir is the new data location.
- Run the ZWCConfig utility. In the Advance tab, edit the location of temp dir.
- Start the ZWC-MySQL service.
- Start the ZWCService service.
Backing Up Windows Clients
Creating a Disk List Entry (DLE) for a Windows Client
The Zmanda Management Console (ZMC) allows Disk List Entries with different Host Types to be included in the same Backup Set. Disk List Entries for Windows Clients resemble entries for other host types (Linux, Solaris, etc.). 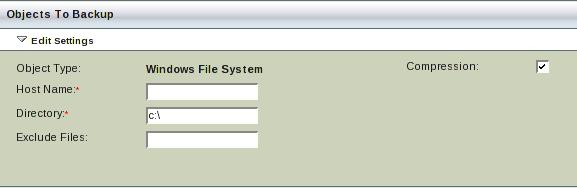
The only way in which Windows clients are treated differently is this: When Windows directory paths are specified by back slashes, ZMC converts them to forward slashes. For example, ZMC converts the path C:\abc to C:/abc. On the Restore What page, all paths are displayed with forward slashes.
Backing up Windows-Mapped Drives
The Zmanda Management Console can back up mapped drives on a Windows client provided the drives have been mapped from the 'amandabackup' account on the Windows machine. This constraint is because XP, Vista, Windows 2003 server drive letters are not global; different users can map different directories on different servers to the same drive letter. For further information, see the article "Backing up network mapped drives on Windows clients" on Zmanda's Knowledgebase.
- Note: The Zmanda Console Manager does not currently support restoring to a mapped drive using the Zmanda Windows Client.
Backing up Windows Applications
If you have purchased and installed the relevant Zmanda licenses, Amanda Enterprise can perform intelligent backups of selected Windows applications such as Exchange and Oracle. These backups use Microsofts VSS (Volume Shadow Service) to capture a consistent copy of the database(s) in question.
Refer to the Zmanda Application Modules User Guide for further details.
Backing Up Hardlinked Files
If only one of the hardlinked files is present in the backup set, then the information about its other hardlink files will not be backed up. Also at restore time, if only one hardlink file is selected for restore, then its other hardlink file will not be restored. Please see this Zmanda Knowledgebase article for details.
Restoring a Windows Client
The Restore procedure for a Windows client similar to the procedure for other clients. Note that you cannot restore a Windows backup to a Linux/Unix destination host.
Completing the Restore Where page for Windows Clients
Destination Host Type
Choose Windows instead of Linux/Unix. 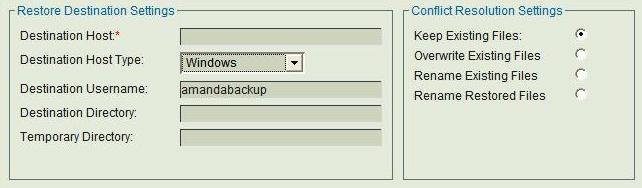
- When the Destination Host Type is Windows, the Destination Username is always amandabackup; the field cannot be edited.
- The Temporary Directory setting has no impact on Windows Client restores.
- If data backed using Zmanda Windows Client is restored to any Host Type other than Windows, the restore fails, returning an error similar to the following error:
- "ERROR: Error uncompressing the backed up data
- This backup cannot be restored to a Linux destination host."
- The following errors are returned if you attempt to restore Linux/Unix backups to a Windows client:
- “ERROR: THE GIVEN BACKUP CANNOT BE RESTORED TO A
- WINDOWS DESTINATION HOST
- ERROR RESTORING THE SELECTED FILES
- RESTORE COMPLETED WITH STATUS FAILURE”
Destination Directory
The Destination Directory specifies the client directory on which ZMC will restore the files (the default is to restore to the original location). If a Restore fails while restoring to Zmanda Windows Client and displays the following error, please refer to the Debug log files located in the Zmanda Windows Client Installation folder for details:
"ERROR: Client Reported Error while Restoring Error restoring the selected files"
Note: Restoring C:\Windows directly is not recommended because the system files may be open. Use a Windows System State backup image (see the next section) to restore files to C:\Windows.
Windows system state backup and recovery
Windows System State refers to a collection of several key operating system elements and their files. Backing up the Windows System State is crucial for a successful disaster recovery strategy. Zmanda Windows Client can back up the Windows System State of Windows 2003 Server (with or without AD), Windows XP, and Vista clients. Windows System State is always a full backup (level 0).
The system state can be restored to the original location or a different location. Partial restoration of Windows System State can be done only to a different directory location. Windows System State files require special handling to back up because they are always locked.
Depending on the type of Windows system, Zmanda Windows Client software backs up the following System State information in comprehensive and coherent fashion:
Workstations
Workstation in this context means any Windows XP machine or any Windows Vista or Windows 2003 server machine which does not have Active Directory (AD).
- Boot Files:
-
- On Windows XP and Windows 2003: SystemDrive\NTDETECT.COM, SystemDrive\ntldr, SystemDrive\boot.ini (SystemDrive is usually c:).
- On Vista: SystemRoot\boot directory (SystemRoot is usually c:\windows)
- Catalog files: SystemRoot\System32\CatRoot\.
- MachineKeys Files: SystemRoot\System32\Microsoft\Protect\* and AllUsersProfile\ApplicationData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeys\* where ALLUSerProfile is c:\Documents and Settings\All Users.
- Performance counters: perf*.dat and perf*.bak files in c:\windows\system32 on all OSs.
- WFP files: All dll and exe files that come under Windows File Protection (WFP). Usually the dll files reside in c:\windows\system32
- IIS metadata file if IIS is installed (applicable to all OSs).
- Certificate Database (Applicable to only Windows 2003 server that are Certificate Servers): files in c:\windows\system32\certsrv
- COM+ registration database.
- Registry: System, default, SAM, Security and Software files in SystemRoot\system32\config and additional Components and Schema files in Vista.
Domain Controllers
A Domain Controller (or DC) is any Windows 2003 machine with Active Directory installed. DC backups include all of the state information listed above for Workstations, plus the Active Directory database, log files, and Group Policy Objects (GPOs).
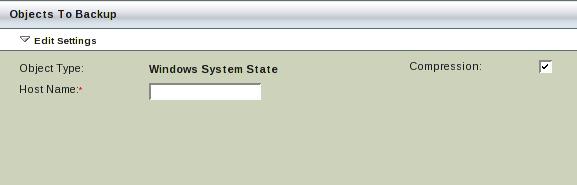
Windows System State Backup from the ZMC
To back up the Windows System State (which is always a full backup), choose Microsoft Windows System State as the type in the Backup What page of the Zmanda Management Console. Compression of system state can be enabled by clicking the check box on the right panel.
Windows System State Restore from the ZMC
To restore Windows system state, specify the Initial Directory as SystemState in the Restore What page of ZMC.
Please note the following requirements and cautions regarding System State restores through the Zmanda Windows Client:
- The System State backup source Windows version, platform (i.e. whether it is 32- or 64-bit) and Service Pack level must match those on the target system. For example, you cannot restore a System State backup taken from an XP system to a Vista system, nor can you restore a 32-bit System State backup to a 64-bit target even if the Windows versions match.
- If restoring the System State backup to the original source of the backup, you must restore all components of the system state; partial restores are possible only to a different destination directory.
- Windows 2003 Active Directory restores are non-authoritative by default. To perform an authoritative AD and SYSVOL restore, follow the steps here. The Zmanda Windows Client does not directly support authoritative AD/SYSVOL restore.
- For System State restore to a Domain Controller (provided AD is already installed), you must reboot the machine in Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM), and then manually start the ZWCService using the DSRM or "Local System"account, then run the System State restore.
- If Active Directory is not installed, then Restoring System State does not require the system to the be in Directory Services Restore boot mode.
- Even if the System State restore is not to the original location, the OS versions must match. If the System State that contains the AD database & restore is not to the original location, then the System does not need to be booted in Directory Services Restore mode.
- If restoring to the entire system state to the original backup source, you must reboot the machine to complete the System State restore.
Changing the password for the amandabackup user
During the installation process, the amandabackup user is created and a password is set. To change the password, shut down the Zmanda Windows Client service, then use the Windows Control Panel utility to edit the amandabackup user account. Use the same procedure as for any other Windows-based password protected service. Restart the Zmanda Windows Client service when you are done. Note that the service must restart without any errors for the changed password to take effect.
Zmanda Windows Client configuration utility
The Zmanda Windows Client configuration utility (ZWCConfig) can be used to change Windows client logging levels, adding/removing Amanda servers and to create windows templates. A template is a list of directories on the Windows client that are to be backed up as group, offering the same functionality that Disk List Entries provide on the Amanda server.
Log on to the workstation as the Administrator and start ZWCConfig utility by clicking Start->Programs->Zmanda Client for Windows->ZWCConfig. To create a template, click the Template tab. Specify a template name and the list of files and folders to be included in the template. The following screen shows the creation of mydocs template that backs up the adminstrator's documents folder.
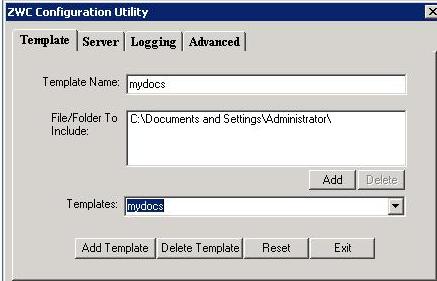
The Zmanda Windows Client templates can be added to Amanda client configuration using Zmanda Management Console. Navigate to Backup Where and choose Windows Template as the object to backup to display the following:

Host Name is the name of the Window system being backed up, which can be either an IP address or a fully qualified domain name. Template specifies the path to the template file on that host. See the ZMC's Backup What help for more detailed information about the other fields and ZMC operation.
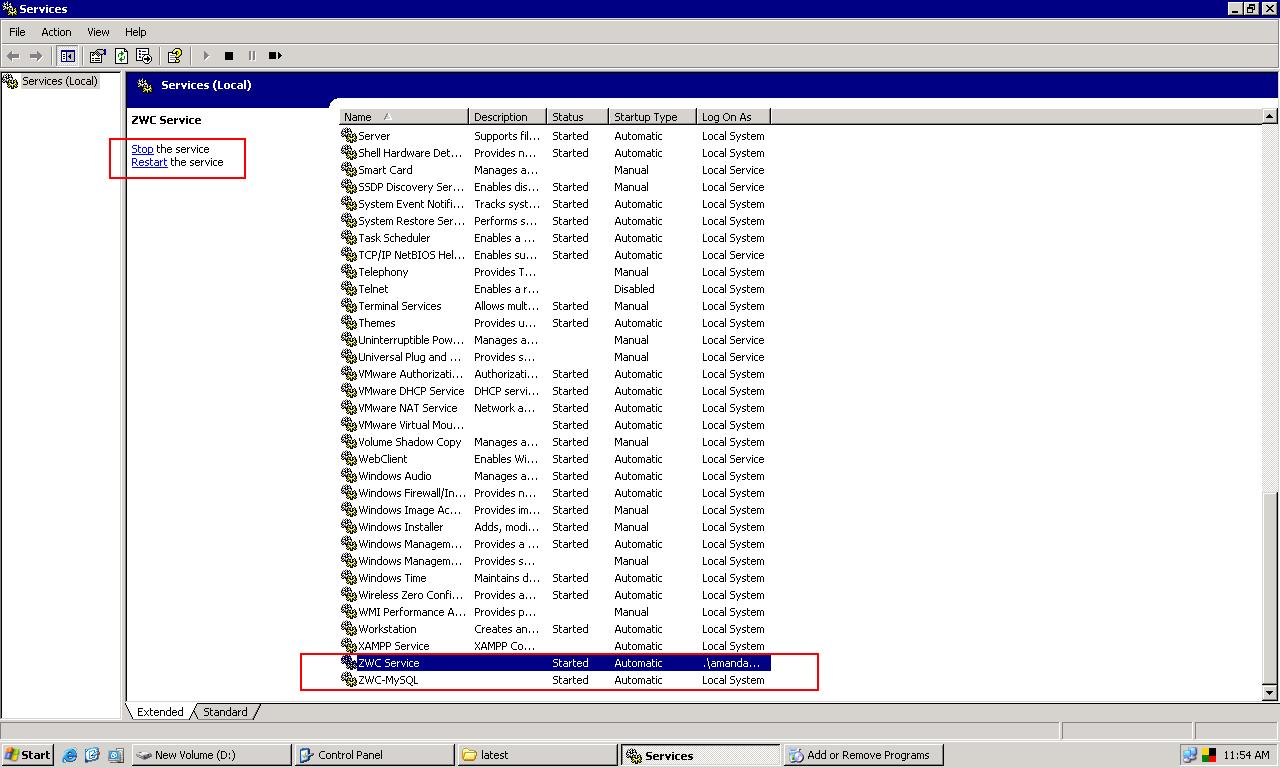
Changing ZWC configuration parameters requires administrator to restart Zmanda Windows Client service. Zmanda Windows client service can be restarted from the Windows services user interface (Administrative Tools > Services). An example services screen is shown below.
Invoking Pre- and Post-backup Scripts
You may have a need to perform automated operations before and after a backup run, such as deleting temporary files, starting or shutting down services, or other such operations that can be performed from a Windows script or batch file. By editing the template file described in the previous section, you can specify such scripts to run automatically either before or after a backup run for a given backup set.
Simply add a <PRE_BACKUP_SCRIPT> or <POST_BACKUP_SCRIPT> tag to the template.txt file for a given backup set. The tag's content is the path to script. For example:
<DLE_Template>
<DLE_NAME>juventus</DLE_NAME>
<DLE_TYPE>USER-DEFINED</DLE_TYPE>
<FILE_LIST>
<FILE_NAME>c:\data</FILE_NAME>
</FILE_LIST>
<PRE_BACKUP_SCRIPT>C:\preScript.bat prebackup.txt</PRE_BACKUP_SCRIPT>
<POST_BACKUP_SCRIPT>C:\postScript.bat postbackup.txt<POST_BACKUP_SCRIPT>
</DLE_Template>
If the prebackup script fails, the backup returns ZWC_ENG_ERR_PRE_SCRIPT (error code 278).
If the postbackup script fails, error will be logged and backup status will be success.
Compatibility with previous versions of the Zmanda Windows Client
If you have created backup images using Amanda Enterprise edition Windows Client 2.6.1 or older, the older version of the client is required to recover the files to a Windows machine. Contact the Zmanda Support team for assistance. Alternatively, you can use the current version of Amanda Enterprise to recover the files to the backup server and then move them manually to the client.
Running the Windows Client Support Script
The zwc-support utility collects system log files, log files related to ZWC and system related information. The utility then archives these log files into a single compressed file. This compressed file can be then sent to the Zmanda Support team for analysis.
Location
The Zmanda Windows Client support utility zwc-support.bat is included with the Zmanda Windows Client. To start the script, click Start->Programs->Zmanda Client for Windows->zwc-support
Files Gathered
The following types of log files are gathered by zwc-support:
Zmanda Windows Client Installation Logs
- c:\ZWC_install.log
- C:\Program Files\Zmanda\Zmanda Client for Windows\Debug\LogFile.txt
Zmanda Windows Client Debug Logs:
- C:\Program Files\Zmanda\Zmanda Client for Windows\Debug\LogFile(n).txt
- Zmanda Windows Client configuration info
System Logs:
- System-info
- Application and System Logs
Additional information:
- Files and Folders count on all the drives.
- Environment variables list.
- MySQL dump
Output File
After the utility is run, an output file with the name zwc-logs-datetimestamp.cab is created in the Zmanda installation directory.
