Microsoft SQL Server Backup
This chapter provides information on how Amanda Enterprise backs up Microsoft SQL server. It also provides information on how to configure SQL server backups, perform backup and recovery of SQL server. The last section provides an example on how to configure Amanda Enteprise for disaster recovery of a Windows server running Microsoft SQL server.
When the Zmanda Client for Windows is configured and licensed for Microsoft SQL backup, it uses the Microsoft Volume Shadow Services to back up the SQL database(s) and logs. Depending on which service is enabled on the server, ZWC uses either the SQL Server VSS Writer or the MSDE Writer.
ZWC can perform full and differential backup of databases and transaction log files using Volume Shadow Services. Log only backups are not supported.
ZCB supports Simple Recovery Model, Full Recovery Model and Bulk Recovery Model for SQL server databases. If the database is in Simple Recovery Model, the full backup will contain .MDF, .LDF and .NDF (in case of filegroups) files in the backup image. The differential backup will contain .LDF files. If the database is in Full Recovery Model, the full backup will contain .MDF, .LDF and .NDF (in case of filegroups) files in the backup image. The differential backup will contain .MDF-Offset (partial file of .MDF database that has changed), .LDF and .TRN (transaction logs flushed to the disk) in the backup image. If the database is in Bulk-log Recovery Model, the full backup will contain .MDF, .LDF and .NDF (in case of filegroups) files in the backup image. The differential backup will contain .MDF-Offset (partial file of .MDF database), .LDF and .TRN (transaction logs flushed to the disk) files in the backup image.
The master database is only backed up as part of the full backups. During restore of master database, SQL server is stopped and is restarted after restoration.
Requirements for Microsoft SQL Server Backup and Restore
These instructions assume you have already installed and licensed the Amanda Enterprise server and the Microsoft SQL Server being backed up. There are a number of additional requirements:
- Make sure that your versions of Windows and SQL Server conform to the tested platforms listed on the Zmanda Network Supported Platforms page.
- The Volume Shadow Copy Service must be enabled. This means that its startup type must be either automatic or manual.
-
The amandabackup SQL user must be created. This user is used to perform backup and recovery. Appropriate permissions for backup and recovery must be provided for this user. Use SQL Management Studio: Go to Security->Logins->add new login->add the amandabackup user account and give it necessary permissions for backup and recovery. Alternatively, you can add it to the sysadmin server role.
- ZWC will only back up MS SQL databases that are in Mounted state.
- Microsoft recommends that MSSQL and System State back ups should not be run simultaneously.
- ZWC only backs up the MS SQL databases. It does not back up other MSSQL files such as program installation files, SSL certificates etc. To protect an MS SQL server from a disaster, make sure that you create a separate disk list entry to back up the other crucial MS SQL files.
- ZWC does not support component-based backup. It backs up all the mounted databases in the MSSQL server.
- For MS SQL server 2000, only full backups are supported. Block level differential backup is not supported because SQL server 2000 VSS writer does not return changed block information.
Configuring Microsoft SQL Server Backups from the ZMC Backup What Page
Create a dedicated backup set for each Microsoft SQL Server you intend to back up. On the Backup What page you are prompted to select what type of object you want to back up. Choose mssql, and the following options are displayed:
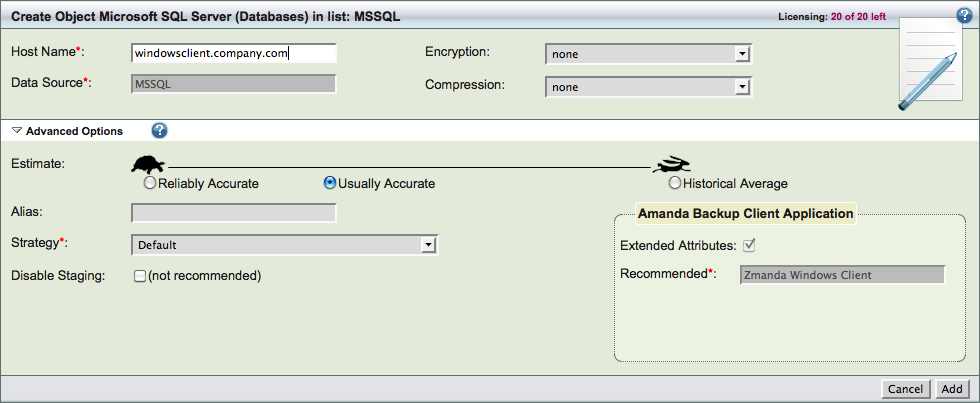
- Host Name
- The name of the machine running the Microsoft SQL server you intend to back up.
- Data Source
- The data source has to be MSSQL and cannot be changed.
- Compression
- Select where compression should be performed - Server or Client and How it should be performed - fast or best.
- Encryption
- Select where encryption should be performed - Server or Client.
After you have set the options, click the Add button to add the Microsoft SQL Server object to the backup set. ZMC will perform automatic configuration check when the object is added to the backup set. You can then configure the backup set just as you would any other by setting the options on Backup Where, Backup How, and Backup When, etc.
Please make sure no other backup software is scheduled to run at the same time as the Amanda SQL server backup.
When the backup starts, the Zmanda Windows Client collects a list of mounted databases (including their physical paths) from the SQL Writer. ZWC then takes a snapshot of the drives on which the databases are located. During snapshot creation the SQL Writer stops all I/O operations to the databases. Once the snapshot is done, the SQL Writer resumes I/O operations, and ZWC takes a backup of the database files from the snapshot volume. The snapshot is deleted after the backup is completed.
Configuring Microsoft SQL Server Restores from the ZMC
When you have selected the disk list entry that includes the MS SQL databases for restore, the Restore What page displays the following options:
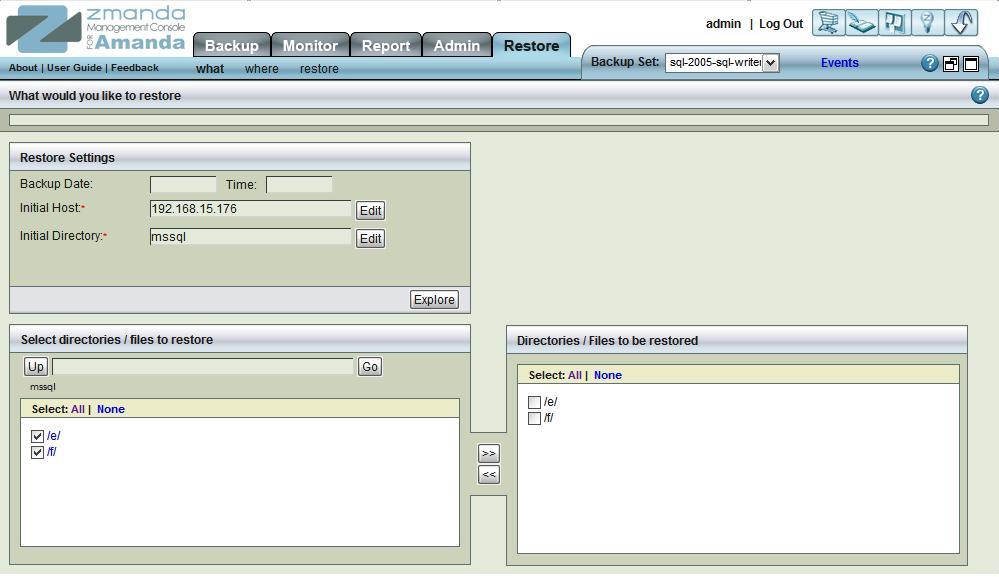
Select all the host databases and log files on the Restore->What page. Click Next to display the Restore Where page:
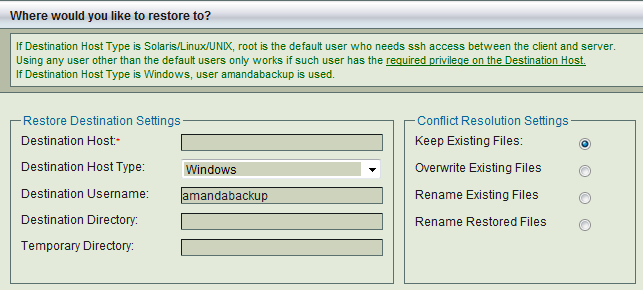
- If restoring to the original server, make sure that MS SQL is installed in the same location as when the backup was run. The databases and log file locations should also match the original configuration. When no directory is specified in the '''Restore Where''' page, the Zmanda Windows Client stops the host SQL services before beginning the restore, and re-starts after the restore is complete. You must then recover the databases on the server manually.
- If restoring to an alternative location, simply specify that directory. The ZWC will then perform a simple copy operation without attempting any pre- or post-restore operations. No SQL recovery is required in this type of restore.
Troubleshooting
If an MS SQL backup fails, follow these troubleshooting steps:
- Check the Windows Event Viewer for any VSS or SQL Server VSS Writer or MSDE Writer errors. Run the command vssadmin list writers at the Windows command prompt and check that the SQL Server VSS/MSDE Writers are in a stable state. If not (or if there are any VSS errors, restart the Writers and Volume Shadow Copy Service).
- Make sure that the SQL databases are in Mounted state.
SQL server Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery refers to restoring the system and data in the event of partial or complete failure of a computer because of natural or technical causes. Following sections explain how to prepare for Disaster Recovery of a server running Microsoft SQL server and recover the system as part of Disaster recovery.
Backups for Disaster Recovery
Use Amanda Enterprise to configure backups of the following server components as separate DLEs in the ZMC Backup What page. It is recommended that all these DLEs are in the same backup set.
Perform a backup of the System drive i.e. the drive where Windows is
Installed. In most of the cases, it will be C:\.
2. Perform a backup of the SQL installation directory. In case, it is a default
installation, SQL installation path will be "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL
Server". Exclude the Database and log files directory, since they need to be
backed up separately.
3. Perform a System State backup.
4. Perform a backup of Microsoft SQL Server database using the "Microsoft SQL
Server" option in the "Backup > What" page.
To recover the SQL Server after a disaster, perform the following steps:
1. Install the original version of Windows. Make sure that the new server has
exact same drive partitions, Filesystem (like NTFS), Windows installation
directory, Computer Name as the original server. Do not join any domain or
Workgroup.
2. Install Zmanda Client for Windows in the same location as the original
server.
3. Through the Zmanda Management Console, go to the Restore > What page.
# Using the "Alias/Directory/Path" field select the System Drive eg
"C:\" from the list.
# Click on "Express Restore". This will automatically restore all the
data from the last Full backup time till the time of the latest backup.
# On the Restore->Where page, enter the details of the destination SQL
Server in the Destination Host field, and fill the rest of the form out as
follows:
- Enter the Destination Username if it is something other than
amandabackup.
- Select Original Location radio button.
- Review the Restore From and Restore To settings on the
Restore->Restore page. Once confirmed, click Restore to start the restore
process.
4. Similarly restore the SQL installation directory.
5. After the System Drive is restored successfully, restore the System State
data. Reboot the server after the System State data is restored successfully.
6. Once, the Server is rebooted, it will have the same Computer name,
Domain/Workgroup, users, groups, etc as the Original server. All the
applications will also be in an installed state.
SQL Recovery:
7. At this time, the SQL Server will be installed but will not be in a running
state since the master & model databases have not been restored yet.
The next step is to restore the master & model databases from the Full
backup. In the Reports Summary page, click on the timestamp link for the Full
backup run.
Clicking on a Timestamp link go to the Restore What page with the date and
time automatically filled in.
# Select the files for master & model databases for restore.
# On the Restore->Where page, enter the details of the destination SQL
Server in the Destination Host field, and fill the rest of the form out as
follows:
- Enter the Destination Username if it is something other than
amandabackup.
- Select Original Location radio button.
- Review the Restore From and Restore To settings on the
Restore->Restore page. Once confirmed, click Restore to start the restore
process.
8. After the databases have been restored to the original location, start the
SQL Instance services. SQL will auotmatically run a recovery and start the SQL
instance.
9. Once SQL Instance is in the running mode, the other databases will need to
be restored. One can also restore the Differential backips.
Please follow the "Restoring to the Original Server:" section to restore the
Full and Differential backup runs.
Note: Using the above procedure, VSS will automatically run a recovery of
the SQL databases and bring them to a consistent state.
