MySQL Configuration
To be able to take advantage of LVM snapshots, the mysql data must reside on logical volumes. The following are some of the possible configurations
- All MySQL data is on a single logical volume
- Specific database directories are on different logical volumes
- For databases containing InnoDB based tables, the lvm snapshot can only be used if the database directory, the InnoDB data files and the InnoDB logs are on logical volumes.
- The InnoDB shared data files are on a separate logical volume
- The InnoDB logs are on a separate logical volume
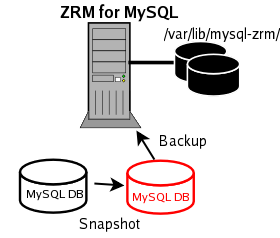
Pre-conditions for Using LVM Snapshots
- The MySQL backup user must be granted sudo privileges to execute lvm commands on the MySQL server. Add a line similar to the following example to /etc/sudoers on the MySQL server:
mysql ZRMserver.mycompany.com Server>=NOPASSWD:/bin/mount,NOPASSWD:/bin/umount,NOPASSWD:/bin/df, \
NOPASSWD:/sbin/lvdisplay,NOPASSWD:/sbin/lvcreate,NOPASSWD:/sbin/lvremove
- where ZRMserver.mycompany.com is the fully-qualified domain name for the ZRM server. Note that if lvm commands are installed in non-standard locations, the above example would not work without editing it to reflect the different paths.
- Additional free extents in the logical volume are needed for creating snapshots.
- This can be checked with 'vgdisplay' command.
- The free extents required are specified in mysql-zrm.conf.
- Note that during the process of creating the backups the disk space may fall short.
- LVM stores the snapshot blocks corresponding to the blocks that are modified in the original logical volume in the snapshot volume.
- If the database is highly active during the backup, many blocks will be modified and snapshot volume may run out of space.
- Specifying the right amount of space for creating the snapshot is critical; if the snapshot volume runs out of space, the backup will not be consistent.
- All MySQL database files (data, log, indexes) must be stored in LVM logical volumes to ensure consistency.
- If any of the files are not on LVM, the snapshot is skipped, and either a raw backup via mysqlhotcopy or a logical backup using mysqldump will be taken based on the storage engines of the tables in each of the databases.
Configuration Parameters
The "Backup How" page allows you to select LVM snapshots as a backup mechanism, and then specify the size of the snapshot volume to be created.
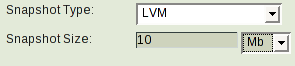
The above will create a snapshot of size 10 MB during the backup run. Please see Backup Parameters for more details.
Note
- This option is ignored if the backup-mode is logical.
Advantages of Using LVM Snapshots for Backup
- Hot backup for transaction based storage engines (no impact on the application using the database) and Warm backups for other storage engines.
- Backup time is not dependent on the size of the database. As a result, this backup method is suitable for large databases.
- Almost instantaneous. The database gets locked only for the time taken to create the snapshot.
Disadvantage of Using LVM Snapshots for Backup
- Works well only for filesystems that support freeze operation such XFS, VxFS.
- Additional disk space for logical volume snapshots is required.
- LVM snapshots can be used only for local backups.
