Table of contents
MySQL Configuration Requirements
To take advantage of VxFS storage checkpoints, all MySQL data and logs must reside on VxFS volumes. The following are some of the possible configurations
- All MySQL data is on a single VxFS Volume
- Specific database directories are on different volumes
- For databases containing InnoDB-based tables, the snapshot can only be used if the database directory, the InnoDB data files and the InnoDB logs are all on VxFS volumes.
- The InnoDB shared data files are on a separate VxFS volume
- The InnoDB logs are on a separate VxFS volume
Refer to Veritas-supplied VxFS documentation for details on VxFS storage checkpoint configuration.
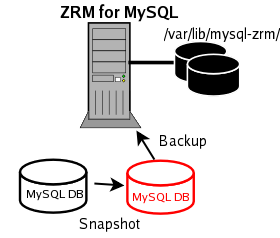
The VxFS volumes are mounted on ZRM server using NFS. ZRM user "mysql" should have permissions to read and write to the volumes.
Pre-conditions for Using VxFS Snapshots
- The MySQL backup user must be granted sudo privileges to execute VxFS commands on the MySQL server. Add a line similar to the following example to /etc/sudoers on the MySQL server:
mysql ZRMserver.mycompany.com Server>=NOPASSWD:/bin/mount,NOPASSWD:/bin/umount,NOPASSWD:/bin/df, \
NOPASSWD:/sbin/fsckptadm
- where ZRMserver.mycompany.com is the fully-qualified domain name for the ZRM server. Note that if VxFS commands are installed in non-standard locations, the above example would not work without editing it to reflect the different paths.
- All MySQL database files (data, log, indexes) must be stored in VxFS volumes to ensure consistency. If any of the files are not on VxFS volumes, a raw backup using mysqlhotcopy, or a logical backup using mysqldump will be taken based on the storage engines of the tables in each of the databases.
