Table of contents
- 1.1. Backup How
- 2.
The Backup how page lets you specify the backup method along with other options that let you optimize the type of backup given the performance required at your site.
All configuration parameters can be configured by selecting the links from the left panel - Backup Method, Backup Alerts/Logging, Compression/Encryption, Remote Backups and Pre/Post Backups. The Backup How page below shows the Backup Method selected and configured for Netapp Snapvault backup method.
Most of the settings have default values, inherited from the Site Settings page or from factory defaults. Default strings are shown in the text field with a gray background. Radio buttons options (Yes, No, Default) show the current default value in parentheses to the right of the Default radio button (Y or N).
- 2.1.1. Backup Method
- 3.
The backup method defines which method to use for full backups. ZRM supports different methods to perform full backups. Each backup set can have different full backup method. Each full backup method is described in a separate section. Snapshot backup methods are described in the next chapter.
- 3.1.1.1. Logical backup using mysqldump
- 4. Following screenshot shows the logical full backup method. The databases/tables in the backup set are locked for updates during the backup process. The backup image contains SQL statements that can be changed if needed. Choosing Logical non-parallel option uses a mysqldump backup that copies MySQL binary logs regardless of the storage engine. MySQL binary logs track and save all database server transactions as a list of SQL statements. To implement a logical backup strategy, binary logging must be enabled on the MySQL server, and a path to the log files must be supplied (the default is /var/lib/mysql) in the Binary Log Path field. Logical backup method works with all MySQL storage engines except the MySQL cluster NDB storage engine. Logical backups can also be restored to any platform architecture or database that supports SQL. For example: Backups of MySQL database running on Redhat Enterprise server powerpc platform can be restored to Ubuntu server running on x86 platform. Because logical backups require a read lock on the database(s) or tables being backed up (not in the case all tables are using InnoDB storage engine), they can have a greater impact on the applications using the MySQL database. Logical backups also result in increased restore times, as restoring the data is accomplished by re-playing the transactions against the target database instead of just copying files. In case of InnoDB tables, the backups are performed as a single transaction and will not obtain any locks. Locking Options When the backup set contains MyISAM tables, the lock-tables option should be selected. When the backup set contains only InnoDB tables, the single-transaction option should be selected. Logical backup of mixture of InnoDB tables and MyISAM tables in the same backup set should be avoided. Logical Backup Options Parameters to the mysqldump MySQL command. Logical backup uses mysqldump command. You can customize the options using this field. For example: "--max_allowed_packet=1G" can be specified as value. These parameters are used in addition to parameters passed by ZRM. Default Character Set Specify the default character set that is used in the MySQL database. The default value is utf8; if the database uses a different character set, reset accordingly. Binary Log Path Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used. If the Site defaults page does not have binary log location specified, binary logs are expected to be in MySQL server datadir location. Flush Logs If you are backing up cloud database services (or when you do not have control over database server configuration) such as Amazon Relational Database services, you should set this parameter to No. Cloud database services does not allow end users to perform MySQL server operations. This parameter is applicable only for full backups. Include Stored Routines To improve the performance of database functions and procedures, MySQL versions 5.0 and higher allow users to compile and store them as reusable routines (Stored routines). This option specifies whether stored routines should be include during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter. On-The-Fly (OTF) Compression Specify whether backup image files stored on disk should be compressed as the backup progresses. The default is to start compression only after all backup files have been saved to disk. Turning this option on can save disk space, but results in slower backups.
- 5.
Users can perform Logical full backups using MyDumper (Download it from https://launchpad.net/mydumper) command. You have to select Full Backup Method as Logical and Logical Parallel as Yes as shown below.
Parallel Logical Backups can work with InnoDB and MyISAM storage engines. Read locks are obtained in case of MyISAM tables. If the backup set only has InnDB tables, locks are not used during backup and MySQL transactions are not impacted.
Logical Backup Options
All MyDumper options are set in this field. These parameters are passed to MyDumper command during full backups.
Include Triggers
This option specifies whether database triggers should be included during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter. The triggers are backed up only if the backup set contains databases (not specific tables).
Include Stored Routines
To improve the performance of database functions and procedures, MySQL versions 5.0 and higher allow users to compile and store them as reusable routines (Stored routines). This option specifies whether stored routines should be included during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter. The stored procedures are backed up only if the backup set contains databases (not specific tables).
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
- 5.1.1.1. Raw Backup Method/without snapshots
- 6.
A raw backup makes a copy of the binary disk image of databases stored on non-transactional storage engines by using mysqlhotcopy. Although raw backups can be restored more quickly than logical backups, they can only be restored to same version of MySQL server on the same platform architecture. If any of the databases or tables are stored on a transactional storage engine (such as InnoDB), a logical mysqldump backup is taken instead unless snapshot backup method is configured.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
- 6.1.1.1. MySQL Enterprise Backup
- 7.
MySQL Enterprise Backup (MEB) tool available from Oracle (requires license from Oracle) can be used as the backup method for the backup set. Full, Differential and Chained differential backups can be performed using this tool. The mysql-zrm.conf parameter apply-log parameter should be to zero to perform differential and chained differential backups.
Select MySQL Enterprise Backup as the full backup method to use MySQL Enterprise Backup to perform the backup. MySQL Enterprise Backup tool is bundled as part of MySQL Enterprise Server Standard edition or premium versions. This option provides integration between ZRM and the Oracle product.
Above image shows the full backup method configured as MySQL Enterprise Backup.
Backups done by particular version of MySQL Enterprise Backup can be restored only by the same version of MySQL Enterprise Backup.
MySQL Enterprise Backup binaries must be installed on the ZRM server in the same location as MySQL server under the following use cases: streaming backup mode (default configuration) and when apply logs are performed during restores (apply-log parameter should be set to 0 in the backup set's mysql-zrm.conf).
MEB Mode
Regular or Streaming mode. Regular mode requires additional disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode does not require disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode requires the MySQL Enterprise Backup 3.6 or higher.
MEB Binary Path
Path to the InnoDB Hot Backup tools: the ibbackup binary and the mysqlbackup tool, which must be installed in the same path on the MySQL server being backed up and ZRM server. The default path is /usr/bin. Themysql user should have permissions to execute the mysqlbackup tool.
MEB disk (I/O throttle)
MEB disk throttle can be specified to throttle disk I/O during backup. It is specified in milliseconds, the backup sleeps for that time between disk I/O.
MEB Use Memory (in MB)
Amount of memory on the MySQL server that can be used MySQL Enterprise Backup. The default is to use as much as memory as available. If you reduce the memory available for MEB significantly, the backup performance will have significant impact.
MEB only InnoDB
MySQL Enterprise Backup tool is used for backups of tables with InnoDB storage engine only. The default is No.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
MEB Only Table Backup
This option is applicable only MySQL 5.6 or later servers. If set to Yes, database tables can be selectively restored. Default is No. It should not set for backing up MySQL server running 5.5 or earlier.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
- 7.1.1.1. XtraBackup
- 8.
Select XtraBackup as the backup method to Xtrabackup tool to perform the backup. Xtrabackup tool can be downloaded from Percona or SkySQL. It is open source and can be downloaded to MySQL server. This option provides integration between ZRM and Xtrabackup. This allows backup to proceed without setting any locks or impacting database operation.
Full, differential and chained differential backups are performed using this tool. The mysql-zrm.conf parameter apply-log parameter should be to zero to perform differential and chained differential backups. This tool also users to restore a table from a database backup. Restores of table can be performed only to Percona MySQL servers.
Xtrabackup binaries must be installed on the ZRM server in the same location as MySQL server under the following use cases: streaming backup mode (default configuration) and when apply logs are performed during restores (apply-log parameter is set to 0 in the backup set's mysql-zrm.conf). Differential backups cannot be performed in Xtrabackup streaming backup mode. Use log incremental with Xtrabackup streaming full backup.
Backups done by particular version of XtraBackup can be restored only by the same version of XtraBackup tool.
XtraBackup Mode
Regular or Streaming mode. Regular mode requires additional disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode does not require disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Xtrabackup 1.6 or higher is required for streaming mode.
XtraBackup Binary Path
You must then supply the path to the Xtrabackup tools: the xtrabackup binary and the innobackupex tool, which must be installed in the same path on the MySQL server being backed up. The default path is /usr/bin. The mysql user should have permissions to execute the innobackupex tool.
XtraBackup Use Memory (in MB)
Amount of memory used by Xtrabackup tool. The default is 100MB.
XtraBackup Parallel
Specifies the number of threads created by xtrabackup to copy data files. This option is useful when multiple tablespaces option is enabled (innodb_file_per_table MySQL server option) or the shared tablespace must be stored in multipe ibdata files with the innodb_data_file_path MySQL server option. The default is 1.
Throttle (in I/O per second)
Xtrabackup backups can be throttled by specifying the number of disk I/Os performed by the backup tool in a second.
XtraBackup No Lock
Use --no-lock option of Xtrabackup. Use this only if you are not planning to do log incremental backups and all your tables in the database are InnoDB.
XtraBackup Default File
If you want to use different my.cnf when xtrabackup starts up the InnoDB during backup. This is required if you are allowing on secure access to the database server.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
- 8.1.1. Backup Alerts/Logging
- 9.
Select Backup Alerts/Logging to send email notifications and control log verbosity.
Email Address (or Update Windows Event Log on Windows servers
On Linux/Solaris servers, enter the email address of the ZMC backup administrator. All backup run notifications and summary reports will be automatically sent to the email address based on the email policy. A mail user agent (MUA) such as Mailx must be manually configured on the MySQL server before any email can be sent. To email reports and notifications to more than one user, set up a group email alias on your mail server and enter group email alias here. Alternatively, you can enter multiple email addresses separated by space. For example:[email protected] [email protected] Windows ZRM servers, select whether to use the Windows Event Log to save and display notifications and summary reports. Note that even when logging successful ZRM operations, the Windows Event Log might show error message that "Event Description not found". The "Event description not found" messages can be safely ignored.
Email Policy
This policy determines when email should be sent to the configured Email Address. Policy can be After every backup (the default value), Never (no notification is performed) or Backup with error (when there are failures in the backup run).
Verbose Logging
Verbose logging should turned on or off. Zmanda Support Team will ask you turn on verbose logging for backup sets to troubleshoot problems in a backup set.
MySQL Replication
Specifies whether ZRM for MySQL will use the MySQL Replication facility that has been enabled on the MySQL server that is to be backed up. Backing up a replication slave reduces impact on the production database near zero while backups are in progress. When this option is enabled and the mMySQL server is a replication slave, ZRM for MySQL will back up the master.info, relay-log.info and any SQL_LOAD-* files if they exist. For further details on the benefits of using a replication slave for backup, see this MySQL documentation. Themaster.info and relay-log.info files are described here. Please note that the replication file names have to bemaster.info and relay-log.info. Please make sure relay-log-info-file and
master-info-file parameter in the MySQL server configuration file my.cnf is set to default value.
If you are backing up replication slave, you need to enable log-slave-updates in the replication slave in MySQL configuration file (my.cnf) for log incremental backups.
Copy Binary Logs
By default, ZRM copies binary logs during full backups (Default value is Yes). This allows ZRM to restore to any event between last backup before full backup and the full backup. You can turn this behavior off by setting value to No.
- 9.1.1. Compression/Encryption
- 10.
Backup can be compressed and encrypted. ZRM compression and encryption is performed on the ZRM server.
Compression Backup compression is performed on the ZRM server. Allows you to compress the image using gzip on the ZRM server. If the storage engine already compresses data (such as ARCHIVE storage engine), there is no value in setting this to Yes.Encryption
Backup encryption is performed on the ZRM server. Default encryption is performed using GPG. ZRM server should have GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) packages installed. These packages are part of Linux and Solaris distribution. The default encryption algorithm used is AES 256. If different key length or cryptographic algorithm is required, please modify gpg parameters in the script /usr/share/mysql-zrm/plugins/encrypt-plugin.pl on the ZRM server. Please contact Zmanda support team for help.Path to passphrase file
The full path to the encryption passphrase file. The encryption file is usually stored as /etc/mysql-zrm/<backup set name>/.passphrase on the ZRM server. The passphrase should be owned by mysql user and should have 400 permission. It is very important to protect the contents of the passphrase file. Passphrase file contains the sequence of words or a string that is used for encryption. It is important to choose a good passphrase. The longer and more random the passphrase, the more difficult to crack the encryption. The passphrase file should contain the passphrase in the first line (other lines in the file are not read). A method to generate passphrase is to use the following command:
$ gpg --gen-random 1 16 | gpg --enarmor | sed -n 5p > /etc/mysql-zrm/<backup set name>/.passphrase
Backup Encryption Caution: It is very important to store the encrypt-plugin.pl and the passphrase file used for the backup set. These files are necessary
for restoration. Without these files, it is impossible to restore the backup image and backup image is no longer useful.
- 10.1.1. Remote Backups
- 11.
ZRM uses copy plugins to move data from the MySQL server to the ZRM server. All remote MySQL backups must be use a copy plugin. Copy plugin is used in the following cases:
backing up any Windows-based MySQL server; use the Windows copy plugin. remote incremental backup is required copying replication-related files from a remote machine executing mysqlhotcopy (MySQL command) to copy the data from the remote MySQL server executing mysqlhotcopy to restore the data to a remote MySQL server. backing up remote machines via snapshot backups.
SSH
Secure Shell-based communication. Use when a higher level of security is required (such as when the client and server communicate across a firewall). This can be only used for non-Windows MySQL servers. You must then enter the SSH username on the remote MySQL server, and the path where MySQL commands are installed on the remote machine. For backup, it is necessary to set up password-less ssh configuration is required (i.e,mysql user on ZRM server should be able to ssh to MySQL server without being prompted for password). During restore, users will prompted for ssh password if needed. The user id and group id of mysql user must be same on the ZRM and MySQL server.
Socket
Socket-based communication. This is the default copy plugin. This plugin requires MySQL server running on non-Windows platform. This requires that the ZRM client components are installed on the remote machine, as described in the Installation Instructions. You must then enter a port for the remote socket (the factory default is 25300. The path where MySQL commands are installed on the remote machine must be provided. The user id and group id of mysql user must be same on the ZRM and MySQL server.
You can specify the port to be used for communication. This requires changes in the remote MySQL server installation (xinetd configuration files).
Windows
The Windows copy plugin is required for backing up any Windows-based MySQL server. It requires the ZRM for MySQL Windows client components described in the Installation Instructions. You must then enter the communications ports to use during backup (default is 10080) and restore (default is 10081) operations.
- 11.1.1. Pre-/Post- Backup
- 12. Specify the full path and any command-line options to the script or utility you want executed before the backup run starts (pre-backup) or after the backup run is completed (post-backup). This feature can be used to check and prepare the MySQL server environment for backup. For example, you could use it to notify all MySQL database users that a backup is about to begin. ZRM for MySQL does not check if the path is a valid path, nor if the plugin is present at the given location. The recommended location for plugins is /usr/share/mysql-zrm/plugins directory. A template file (pre-backup.pl or post-backup.pl) is installed in this location; use the template when writing your own pre-backup plugin. All pre-backup plugin scripts must accept the following command-line parameters (which are passed to the plugin using the Plugin Option(s) field: --all-databasesUsed when all databases in the MySQL server are being backed up. --database database1, database2, ... Used when specific databases are backed up. --database database1 --tables table1, table2, ... Used when specific tables in a database are being backed up. The script should be written to return a non-zero value on error; pre-backup plugin failures should cancel the backup and generate a failure message for reports and logs. Post backup plugin are passed an additional parameter with information on location of backup images (--backup-directory path) The post-backup plugin is executed twice: before the checksum is performed, and after the checksum is complete. See the man page for mysql-zrm-backup(1) for more details on how the post-backup plugin operates and the flags it returns. Note that although failures of the post-backup plugin are logged, they are not included in backup reports if the backup itself succeeded. Pre-Scheduler plugin can be used to delay the execution of the scheduled backup run. You can use this plugin to avoid backup during certain operational procedures such as MySQL upgrade or database upgrades. The value returned by the plugin determines how many hours the scheduled execution of backup run is delayed. It can be delayed up to 11 hours. You can optionally compress the data during transport. This might provide better performance.
Backup How
The Backup how page lets you specify the backup method along with other options that let you optimize the type of backup given the performance required at your site.
All configuration parameters can be configured by selecting the links from the left panel - Backup Method, Backup Alerts/Logging, Compression/Encryption, Remote Backups and Pre/Post Backups. The Backup How page below shows the Backup Method selected and configured for Netapp Snapvault backup method.
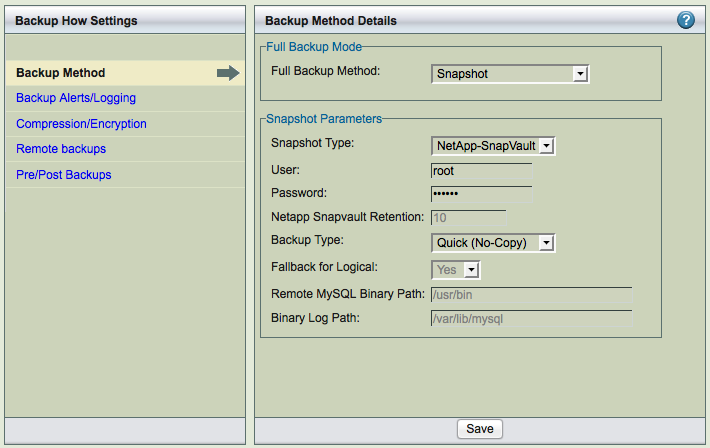
Most of the settings have default values, inherited from the Site Settings page or from factory defaults. Default strings are shown in the text field with a gray background. Radio buttons options (Yes, No, Default) show the current default value in parentheses to the right of the Default radio button (Y or N).
Backup Method
The backup method defines which method to use for full backups. ZRM supports different methods to perform full backups. Each backup set can have different full backup method. Each full backup method is described in a separate section. Snapshot backup methods are described in the next chapter.
Logical backup using mysqldump
Following screenshot shows the logical full backup method. The databases/tables in the backup set are locked for updates during the backup process. The backup image contains SQL statements that can be changed if needed.
Choosing Logical non-parallel option uses a mysqldump backup that copies MySQL binary logs regardless of the storage engine. MySQL binary logs track and save all database server transactions as a list of SQL statements. To implement a logical backup strategy, binary logging must be enabled on the MySQL server, and a path to the log files must be supplied (the default is /var/lib/mysql) in the Binary Log Path field.
Logical backup method works with all MySQL storage engines except the MySQL cluster NDB storage engine. Logical backups can also be restored to any platform architecture or database that supports SQL. For example: Backups of MySQL database running on Redhat Enterprise server powerpc platform can be restored to Ubuntu server running on x86 platform.
Because logical backups require a read lock on the database(s) or tables being backed up (not in the case all tables are using InnoDB storage engine), they can have a greater impact on the applications using the MySQL database. Logical backups also result in increased restore times, as restoring the data is accomplished by re-playing the transactions against the target database instead of just copying files. In case of InnoDB tables, the backups are performed as a single transaction and will not obtain any locks.
Locking Options
When the backup set contains MyISAM tables, the lock-tables option should be selected. When the backup set contains only InnoDB tables, the single-transaction option should be selected. Logical backup of mixture of InnoDB tables and MyISAM tables in the same backup set should be avoided.
Logical Backup Options
Parameters to the mysqldump MySQL command. Logical backup uses mysqldump command. You can customize the options using this field. For example: "--max_allowed_packet=1G" can be specified as value. These parameters are used in addition to parameters passed by ZRM.
Default Character Set
Specify the default character set that is used in the MySQL database. The default value is utf8; if the database uses a different character set, reset accordingly.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used. If the Site defaults page does not have binary log location specified, binary logs are expected to be in MySQL server datadir location.
Flush Logs
If you are backing up cloud database services (or when you do not have control over database server configuration) such as Amazon Relational Database services, you should set this parameter to No. Cloud database services does not allow end users to perform MySQL server operations. This parameter is applicable only for full backups.
Include Stored Routines
To improve the performance of database functions and procedures, MySQL versions 5.0 and higher allow users to compile and store them as reusable routines (Stored routines). This option specifies whether stored routines should be include during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter.
On-The-Fly (OTF) Compression
Specify whether backup image files stored on disk should be compressed as the backup progresses. The default is to start compression only after all backup files have been saved to disk. Turning this option on can save disk space, but results in slower backups.
Parallel Logical Backup using MyDumper
Users can perform Logical full backups using MyDumper (Download it from https://launchpad.net/mydumper) command. You have to select Full Backup Method as Logical and Logical Parallel as Yes as shown below.
Parallel Logical Backups can work with InnoDB and MyISAM storage engines. Read locks are obtained in case of MyISAM tables. If the backup set only has InnDB tables, locks are not used during backup and MySQL transactions are not impacted.
Logical Backup Options
All MyDumper options are set in this field. These parameters are passed to MyDumper command during full backups.
Include Triggers
This option specifies whether database triggers should be included during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter. The triggers are backed up only if the backup set contains databases (not specific tables).
Include Stored Routines
To improve the performance of database functions and procedures, MySQL versions 5.0 and higher allow users to compile and store them as reusable routines (Stored routines). This option specifies whether stored routines should be included during logical backups. The default value is No. If your version of MySQL supports this feature, it should probably be set to Yes. Setting the value to Default implies Site specific value is used for this parameter. The stored procedures are backed up only if the backup set contains databases (not specific tables).
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
Raw Backup Method/without snapshots
A raw backup makes a copy of the binary disk image of databases stored on non-transactional storage engines by using mysqlhotcopy. Although raw backups can be restored more quickly than logical backups, they can only be restored to same version of MySQL server on the same platform architecture. If any of the databases or tables are stored on a transactional storage engine (such as InnoDB), a logical mysqldump backup is taken instead unless snapshot backup method is configured.
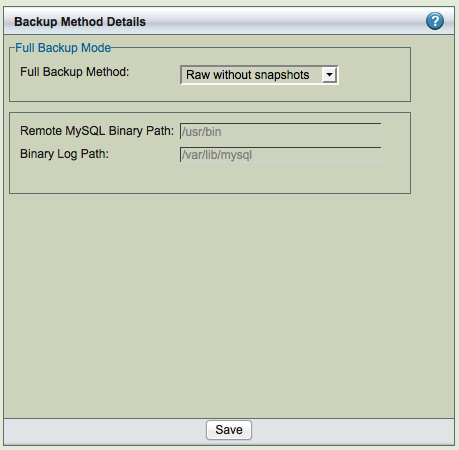
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
MySQL Enterprise Backup
MySQL Enterprise Backup (MEB) tool available from Oracle (requires license from Oracle) can be used as the backup method for the backup set. Full, Differential and Chained differential backups can be performed using this tool. The mysql-zrm.conf parameter apply-log parameter should be to zero to perform differential and chained differential backups.
Select MySQL Enterprise Backup as the full backup method to use MySQL Enterprise Backup to perform the backup. MySQL Enterprise Backup tool is bundled as part of MySQL Enterprise Server Standard edition or premium versions. This option provides integration between ZRM and the Oracle product.
Above image shows the full backup method configured as MySQL Enterprise Backup.
Backups done by particular version of MySQL Enterprise Backup can be restored only by the same version of MySQL Enterprise Backup.
- MySQL Enterprise Backup binaries must be installed on the ZRM server in the same location as MySQL server under the following use cases: streaming backup mode (default configuration) and when apply logs are performed during restores (apply-log parameter should be set to 0 in the backup set's mysql-zrm.conf).
MEB Mode
Regular or Streaming mode. Regular mode requires additional disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode does not require disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode requires the MySQL Enterprise Backup 3.6 or higher.
MEB Binary Path
Path to the InnoDB Hot Backup tools: the ibbackup binary and the mysqlbackup tool, which must be installed in the same path on the MySQL server being backed up and ZRM server. The default path is /usr/bin. Themysql user should have permissions to execute the mysqlbackup tool.
MEB disk (I/O throttle)
MEB disk throttle can be specified to throttle disk I/O during backup. It is specified in milliseconds, the backup sleeps for that time between disk I/O.
MEB Use Memory (in MB)
Amount of memory on the MySQL server that can be used MySQL Enterprise Backup. The default is to use as much as memory as available. If you reduce the memory available for MEB significantly, the backup performance will have significant impact.
MEB only InnoDB
MySQL Enterprise Backup tool is used for backups of tables with InnoDB storage engine only. The default is No.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
MEB Only Table Backup
This option is applicable only MySQL 5.6 or later servers. If set to Yes, database tables can be selectively restored. Default is No. It should not set for backing up MySQL server running 5.5 or earlier.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
XtraBackup
Select XtraBackup as the backup method to Xtrabackup tool to perform the backup. Xtrabackup tool can be downloaded from Percona or SkySQL. It is open source and can be downloaded to MySQL server. This option provides integration between ZRM and Xtrabackup. This allows backup to proceed without setting any locks or impacting database operation.
Full, differential and chained differential backups are performed using this tool. The mysql-zrm.conf parameter apply-log parameter should be to zero to perform differential and chained differential backups. This tool also users to restore a table from a database backup. Restores of table can be performed only to Percona MySQL servers.
Xtrabackup binaries must be installed on the ZRM server in the same location as MySQL server under the following use cases: streaming backup mode (default configuration) and when apply logs are performed during restores (apply-log parameter is set to 0 in the backup set's mysql-zrm.conf). Differential backups cannot be performed in Xtrabackup streaming backup mode. Use log incremental with Xtrabackup streaming full backup.
Backups done by particular version of XtraBackup can be restored only by the same version of XtraBackup tool.
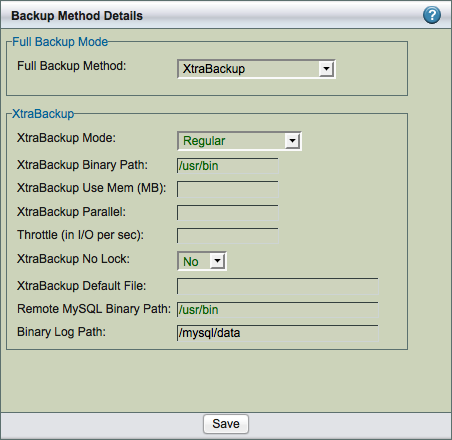
XtraBackup Mode
Regular or Streaming mode. Regular mode requires additional disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Streaming mode does not require disk space on the MySQL server during backups. Xtrabackup 1.6 or higher is required for streaming mode.
XtraBackup Binary Path
You must then supply the path to the Xtrabackup tools: the xtrabackup binary and the innobackupex tool, which must be installed in the same path on the MySQL server being backed up. The default path is /usr/bin. The mysql user should have permissions to execute the innobackupex tool.
XtraBackup Use Memory (in MB)
Amount of memory used by Xtrabackup tool. The default is 100MB.
XtraBackup Parallel
Specifies the number of threads created by xtrabackup to copy data files. This option is useful when multiple tablespaces option is enabled (innodb_file_per_table MySQL server option) or the shared tablespace must be stored in multipe ibdata files with the innodb_data_file_path MySQL server option. The default is 1.
Throttle (in I/O per second)
Xtrabackup backups can be throttled by specifying the number of disk I/Os performed by the backup tool in a second.
XtraBackup No Lock
Use --no-lock option of Xtrabackup. Use this only if you are not planning to do log incremental backups and all your tables in the database are InnoDB.
XtraBackup Default File
If you want to use different my.cnf when xtrabackup starts up the InnoDB during backup. This is required if you are allowing on secure access to the database server.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
Binary Log Path
Enter the full path where the MySQL binary logs are stored once binary logging has been enabled. If nothing is entered here, the site default path is used.
Backup Alerts/Logging
Select Backup Alerts/Logging to send email notifications and control log verbosity.
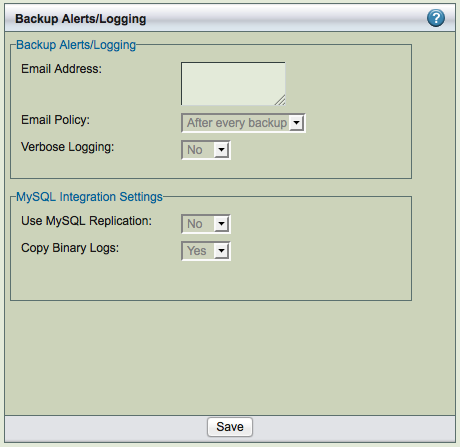
- Email Address (or Update Windows Event Log on Windows servers
- On Linux/Solaris servers, enter the email address of the ZMC backup administrator. All backup run notifications and summary reports will be automatically sent to the email address based on the email policy. A mail user agent (MUA) such as Mailx must be manually configured on the MySQL server before any email can be sent. To email reports and notifications to more than one user, set up a group email alias on your mail server and enter group email alias here. Alternatively, you can enter multiple email addresses separated by space. For example:[email protected] [email protected]
- On Windows ZRM servers, select whether to use the Windows Event Log to save and display notifications and summary reports. Note that even when logging successful ZRM operations, the Windows Event Log might show error message that "Event Description not found". The "Event description not found" messages can be safely ignored.
- Email Policy
- This policy determines when email should be sent to the configured Email Address. Policy can be After every backup (the default value), Never (no notification is performed) or Backup with error (when there are failures in the backup run).
Select Backup Alerts/Logging to send email notifications and control log verbosity.

- On Linux/Solaris servers, enter the email address of the ZMC backup administrator. All backup run notifications and summary reports will be automatically sent to the email address based on the email policy. A mail user agent (MUA) such as Mailx must be manually configured on the MySQL server before any email can be sent. To email reports and notifications to more than one user, set up a group email alias on your mail server and enter group email alias here. Alternatively, you can enter multiple email addresses separated by space. For example:[email protected] [email protected]
- On Windows ZRM servers, select whether to use the Windows Event Log to save and display notifications and summary reports. Note that even when logging successful ZRM operations, the Windows Event Log might show error message that "Event Description not found". The "Event description not found" messages can be safely ignored.
- This policy determines when email should be sent to the configured Email Address. Policy can be After every backup (the default value), Never (no notification is performed) or Backup with error (when there are failures in the backup run).
Verbose Logging
Verbose logging should turned on or off. Zmanda Support Team will ask you turn on verbose logging for backup sets to troubleshoot problems in a backup set.
- MySQL Replication
- Specifies whether ZRM for MySQL will use the MySQL Replication facility that has been enabled on the MySQL server that is to be backed up. Backing up a replication slave reduces impact on the production database near zero while backups are in progress. When this option is enabled and the mMySQL server is a replication slave, ZRM for MySQL will back up the master.info, relay-log.info and any SQL_LOAD-* files if they exist. For further details on the benefits of using a replication slave for backup, see this MySQL documentation. Themaster.info and relay-log.info files are described here. Please note that the replication file names have to bemaster.info and relay-log.info. Please make sure relay-log-info-file and
master-info-file parameter in the MySQL server configuration file my.cnf is set to default value.
- If you are backing up replication slave, you need to enable log-slave-updates in the replication slave in MySQL configuration file (my.cnf) for log incremental backups.
- Copy Binary Logs
- By default, ZRM copies binary logs during full backups (Default value is Yes). This allows ZRM to restore to any event between last backup before full backup and the full backup. You can turn this behavior off by setting value to No.
Compression/Encryption
Backup can be compressed and encrypted. ZRM compression and encryption is performed on the ZRM server.
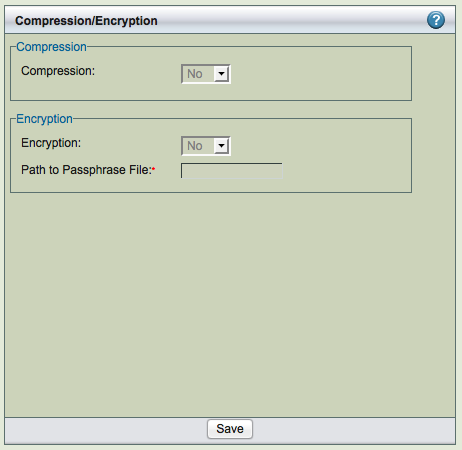
- Compression
- Backup compression is performed on the ZRM server. Allows you to compress the image using gzip on the ZRM server. If the storage engine already compresses data (such as ARCHIVE storage engine), there is no value in setting this to Yes.
- Encryption
- Backup encryption is performed on the ZRM server. Default encryption is performed using GPG. ZRM server should have GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) packages installed. These packages are part of Linux and Solaris distribution. The default encryption algorithm used is AES 256. If different key length or cryptographic algorithm is required, please modify gpg parameters in the script /usr/share/mysql-zrm/plugins/encrypt-plugin.pl on the ZRM server. Please contact Zmanda support team for help.
- Path to passphrase file
The full path to the encryption passphrase file. The encryption file is usually stored as /etc/mysql-zrm/<backup set name>/.passphrase on the ZRM server. The passphrase should be owned by mysql user and should have 400 permission. It is very important to protect the contents of the passphrase file. Passphrase file contains the sequence of words or a string that is used for encryption. It is important to choose a good passphrase. The longer and more random the passphrase, the more difficult to crack the encryption. The passphrase file should contain the passphrase in the first line (other lines in the file are not read). A method to generate passphrase is to use the following command:
$ gpg --gen-random 1 16 | gpg --enarmor | sed -n 5p > /etc/mysql-zrm/<backup set name>/.passphrase
Backup Encryption Caution: It is very important to store the encrypt-plugin.pl and the passphrase file used for the backup set. These files are necessary for restoration. Without these files, it is impossible to restore the backup image and backup image is no longer useful.
Remote Backups
ZRM uses copy plugins to move data from the MySQL server to the ZRM server. All remote MySQL backups must be use a copy plugin. Copy plugin is used in the following cases:
-
- backing up any Windows-based MySQL server; use the Windows copy plugin.
- remote incremental backup is required
- copying replication-related files from a remote machine
- executing mysqlhotcopy (MySQL command) to copy the data from the remote MySQL server
- executing mysqlhotcopy to restore the data to a remote MySQL server.
- backing up remote machines via snapshot backups.
- Secure Shell-based communication. Use when a higher level of security is required (such as when the client and server communicate across a firewall). This can be only used for non-Windows MySQL servers. You must then enter the SSH username on the remote MySQL server, and the path where MySQL commands are installed on the remote machine. For backup, it is necessary to set up password-less ssh configuration is required (i.e,mysql user on ZRM server should be able to ssh to MySQL server without being prompted for password). During restore, users will prompted for ssh password if needed. The user id and group id of mysql user must be same on the ZRM and MySQL server.
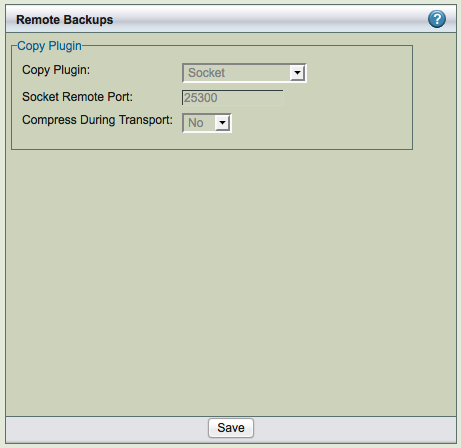
- Socket
Socket-based communication. This is the default copy plugin. This plugin requires MySQL server running on non-Windows platform. This requires that the ZRM client components are installed on the remote machine, as described in the Installation Instructions. You must then enter a port for the remote socket (the factory default is 25300. The path where MySQL commands are installed on the remote machine must be provided. The user id and group id of mysql user must be same on the ZRM and MySQL server.
You can specify the port to be used for communication. This requires changes in the remote MySQL server installation (xinetd configuration files).
- Windows
- The Windows copy plugin is required for backing up any Windows-based MySQL server. It requires the ZRM for MySQL Windows client components described in the Installation Instructions. You must then enter the communications ports to use during backup (default is 10080) and restore (default is 10081) operations.
- Windows
Pre-/Post- Backup
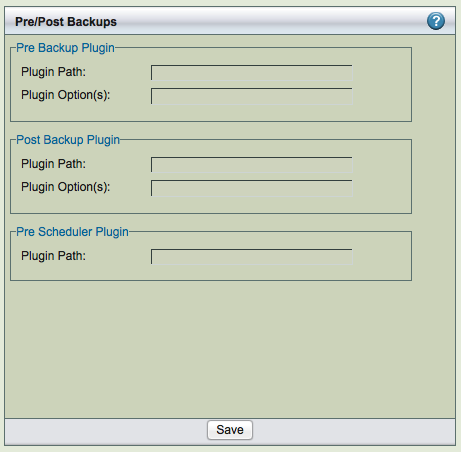
Specify the full path and any command-line options to the script or utility you want executed before the backup run starts (pre-backup) or after the backup run is completed (post-backup). This feature can be used to check and prepare the MySQL server environment for backup. For example, you could use it to notify all MySQL database users that a backup is about to begin.
ZRM for MySQL does not check if the path is a valid path, nor if the plugin is present at the given location. The recommended location for plugins is /usr/share/mysql-zrm/plugins directory. A template file (pre-backup.pl or post-backup.pl) is installed in this location; use the template when writing your own pre-backup plugin. All pre-backup plugin scripts must accept the following command-line parameters (which are passed to the plugin using the Plugin Option(s) field:
--all-databases- Used when all databases in the MySQL server are being backed up.
--database database1, database2, ...
Used when specific databases are backed up.
--database database1 --tables table1, table2, ...
Used when specific tables in a database are being backed up.
The script should be written to return a non-zero value on error; pre-backup plugin failures should cancel the backup and generate a failure message for reports and logs.
Post backup plugin are passed an additional parameter with information on location of backup images (--backup-directory path)
The post-backup plugin is executed twice: before the checksum is performed, and after the checksum is complete. See the man page for mysql-zrm-backup(1) for more details on how the post-backup plugin operates and the flags it returns. Note that although failures of the post-backup plugin are logged, they are not included in backup reports if the backup itself succeeded.
Pre-Scheduler plugin can be used to delay the execution of the scheduled backup run. You can use this plugin to avoid backup during certain operational procedures such as MySQL upgrade or database upgrades. The value returned by the plugin determines how many hours the scheduled execution of backup run is delayed. It can be delayed up to 11 hours.
You can optionally compress the data during transport. This might provide better performance.
