Table of contents
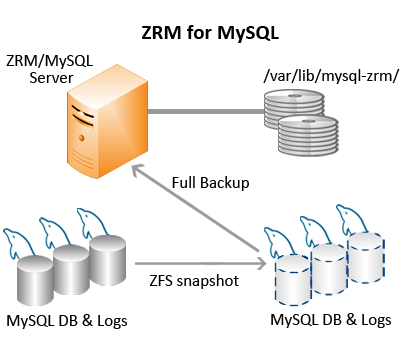
ZFS Snapshots
Sun Microsystem's Solaris ZFS filesystem include snapshot capability, which facilitates near-instantaneous hot backups and rapid restores.
If you purchase the feature license from Zmanda (available at the Zmanda Network Downloads page), ZRM for MySQL & MariaDB includes an optional snapshot plugin that integrates with ZFS to create consistent MySQL full backups. It creates temporary snapshots of the ZFS volumes on which to perform a full backup. When snapshots are enabled, ZRM for MySQL & MariaDB can perform backups with minimal impact on MySQL applications. Database writes will be blocked only during snapshot creation, which typically takes less than a second regardless of database size.
This page describes the configuration of ZFS snapshot backups, including requirements for the MySQL database.
MySQL Configuration Requirements
- Sudo privileges must be configured for mysql user on the MySQL server (see the next section). On Solaris platforms, this means the SMCsudo package must be installed.
- If you are backing up a remote MySQL server, the destination directory specified on the Backup Where page must exist on the MySQL server as well as the ZRM server. The MySQL backup user (OS-level) must have read/write permission to access this directory.
To take advantage of ZFS snapshots, all MySQL database files (data, log, indexes) belonging to the backup set must be stored in ZFS volumes to ensure consistency.
If any of the files are not on ZFS volumes, a raw backup using mysqlhotcopy, or a logical backup using mysqldumpis performed depending on the storage engines of the tables in each of the databases.
Refer to the Solaris ZFS documentation for details on ZFS administration.
Here are some valid scenarios of database storage on ZFS:
- All MySQL data is stored on a single ZFS Volume
- Specific database directories are stored on different volumes
- For databases containing InnoDB-based tables, the snapshot can only be used if the database directory, the InnoDB data files and the InnoDB logs are all on ZFS volumes.
- The InnoDB shared data files are on a separate ZFS volume
- The InnoDB logs are on a separate ZFS volume
MySQL Backup User sudo Privileges
The MySQL backup user (described in System Requirements) must be granted sudo privileges to execute ZFS commands on the MySQL server. Add a line similar to the following example to /usr/local/etc/sudoers on the MySQL server:
mysql MySQLserver.mycompany.com=NOPASSWD:/usr/sbin/df,NOPASSWD:/usr/sbin/zfs
where MySQLserver.mycompany.com is the fully-qualified domain name for the MySQL server. If the MySQL database resides on the the ZRM server, the ZRM server name should be used. Note that if ZFS commands are installed in non-standard locations, the above example would not work without editing it to reflect the different paths. Please see KB article for more information on sudo configuration.
To test the sudo configuration, run the command as the "mysql" user. The command should execute correctly without prompting for a password. For example:
# su - mysql $ /usr/local/bin/sudo /usr/sbin/df
Configuring ZRM for MySQL & MariaDB to use ZFS Snapshots
To activate use of ZFS Snapshots for full backups, simply select the ZFS Snapshot Type for Backup method from the Backup How page:
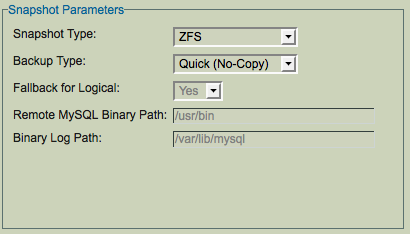
- Backup Type
- Choose the method of snapshot backup. The Standard (Copy) option specifies that the snapshot should be copied to a standard ZRM for MySQL & MariaDB backup archive. The Quick (No Copy) option specifies that the snapshot itself should be used as a near-line backup. Quick backups are convenient as they provide faster backups and restores, but because they remain on the MySQL server they do not protect against media or server failure. Note that if the quick option is specified, the compress and encrypt options are ignored. In addition, no checksums are performed, which means that quick snapshot backups cannot be verified. Quick snapshot backups may be converted to standard backups stored on the ZRM server using the Convert Backup option available from the Reports menu tab.
Fallback for Logical
If this field is set to yes and snapshot backup fails, the logical backup is attempted. Set the value to No if you do not want to do logical backup if there is a snapshot backup failure.
Remote MySQL Binary Path
Path to the MySQL commands on the MySQL server.
Binary Log Path
Location of binary logs on the MySQL server that are used for log incremental backups.
