VMware ESX Server Backup
Amanda Enterprise 3.1 allows you to backup VMware ESX images to various media supported by Amanda. The backups are performed in a file system consistent manner. These backups can be used for restoration of guest VMs running on the ESX server and can be restored to alternate ESX server. The VMware is backed up using VMware Virtual Disk APIs (Vstorage APIs)
Full and incremental backups of the VM are supported. The incremental backups contain only the changed data blocks in the virtual machine.
Zmanda recommends using Amanda client to backup files from guest VM if file level backup of VMs is needed.
Amanda Enterprise VMware ESX application supports licensed (paid) versions of Vsphere 5 and VMware 4.x (or called Vsphere) VMware ESX 3.x is not supported because Vstorage APIs are not available for ESX 3.x. If you are using ESX 3.x, please contact Zmanda support for a solution.
Amanda Enterprise VMware ESX application does not backup VMware independent disks or RDM (Raw Device Mapping) disks. According to VMware, "snapshots of raw disks, RDM physical mode disks, and independent disks are not supported". For more information, refer to the vSphere Basic System Administration guide, Section 17. They have to be backed up by installing Amanda client from another machine.
Requirements for VMware Server Backup and Restore
Software that should be installed on Amanda server
- Amanda server must be running Linux distribution listed on the Zmanda Network Supported Platforms page.
- Amanda Enterprise 3.1.x (including dependencies) must be installed on the Amanda server. Make sure Amanda Enterprise server and Zmanda Management Console is functional before installing and configuring VMware ESX application. Amanda VMware ESX application agent performs the backup from the Amanda server. No additional Amanda client software is required. No software is required on the ESX server.
- Install Amanda Enterprise VMware patches (from Zmanda Network).
- You need to install 32bit or 64bit (depending on the platform architecture) VMware vSphere VCLI (VMware-vSphere-CLI) from VMware and 32bit VMware vSphere VDDK (VMware-vix-disklib) packages only from Zmanda Network (not VMware). These packages have following operating system dependencies:
perl-Crypt-SSLeay
perl-URI
fuse
fuse-libs
curl
openssl-devel
On SLES 11, the above dependencies are required except for the openssl-devel package. Instead of the openssl-devel package, please install the following dependencies from SLES SDK distribution (DVD 1)
libopenssl-devel
zlib-devel
These dependencies can be installed using yum or yast or apt-get tools available in the Linux distribution. The actual names of the packages might be different in different distributions.
On RHEL/CentOS/Oracle Linux systems, you can install these dependencies using:
# yum install fuse-libs fuse perl-Crypt-SSLeay perl-URI curl openssl-devel
On Ubuntu 8.04, following command can be used:
# apt-get install fuse-utils libfuse2 libcrypt-ssleay-perl liburi-perl curl
There are additional dependencies for some Ubuntu platforms. Following packages are also required:
libcrypt-ssleay-perl libclass-methodmaker-perl libxml-libxml-perl libwww-perl psmisc linux-headers-`uname -r`
VMware VCLI is available at the VMware web site. VMware VDDK package is available at Zmanda Network Downloads page. You can install the VMware packages as follows:
# <extract from VMware-vix-disklib tar archive>
# <extract from VMware-vSphere-CLI tar archive>
# ./vmware-vix-disklib-distrib/vmware-install.pl
# ./vmware-vsphere-cli-distrib/vmware-install.pl
Guest Virtual Machine and Other requirements
- All guest VMs being backed up should have Change Block Tracking (CBT) enabled for all the disks. Amanda configuration check in the ZMC Backup What page will automatically enable CBT on the guest VM disks (3.1.3.5 release and later). Please see Zmanda knowledge base article on how to enable Change Block Tracking manually.
- The ESX server must be running on VM hardware version 7 or greater. (Older hardware levels are not supported)
- Amanda VMware ESX application requires temporary space to store the backup images on the Amanda server (See Configuring VMware Server Backups section below). The space required should be equal to the size of the guest VM images being backed up. This space requirement is temporary and required only during backup. The amandabackup user should be able to read and write to this directory on the Amanda server.
- It is also important to remove all VMware snapshots before configuring the guest VM for backups.
- For good backup performance, there should be no snapshots of the Guest VM being backed up.
Installation
Amanda ESX VMware application is installed as part of Amanda server. Separate software is not required. Please install the latest Amanda VMware patch available in Zmanda network.
The application is licensed. Amanda VMware license must be part of Zmanda License file on the Amanda server.
If the VMware commands (vmware-cmd, vmkfs, vmware-diskmanager, snapshotmanager.pl) are not installed in default locations (/usr/lib/vmware-vcli for VCLI and /usr/bin for vmware-diskmanager), you will have to modify /etc/zmanda/zmc_aee/zmc_user_dumptypes to fix the application properties (VCLI-PATH, VCLI-BIN-PATH and VDDK-BIN_PATH).
Configuring VMware Server Backups
Configuring VMware guest VM backups requires steps in both Zmanda Management Console and some manual steps.
- Zmanda recommends creation of separate backup set for backing up guest VM images.
- It is also important to change TEMP-WORKING-DIR location in the /etc/zmanda/zmc_aee/zmc_user_dumptypes file for zmc_vmware_userapp. This location should have sufficient disk space to hold a single uncompressed copy of the largest ESX VMware image that will be backed up. The default value is /tmp/amanda and should be changed because /tmp file system can become full during backup process.
- Create a backup set for the guest VMs in the Zmanda Management Console. Use ZMC Backup What page to add DLEs for ESX servers as shown below. Click Add/Update to save the configuration.
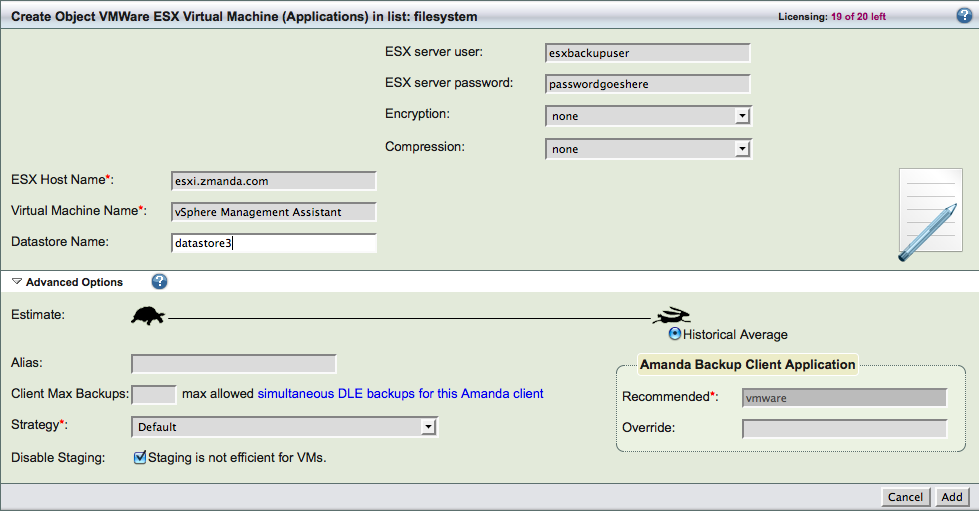
ESX Host Name is the name of the ESX server whose guest VMs are being backed up or the VMware vCenter that manages the ESX server. It can be the IP address or the IP name.
Virtual Machine Name is the name of the guest VM that should be backed up. You should not use the IP address of the guest VM. This is the VM Display name (not the name of the data storage folder on the ESX server) as shown in the left panel in the Vsphere Client. This value is case sensitive. If ESX Host Name is VMware vCenter, the VM can reside on any ESX server managed by the vCenter.
Datastore Name is the name of the VMware datastore used by the guest VM. This field is mandatory.
ESX server user and password is the authentication information for the ESX server or VMware vCenter server. These credentials are used to perform backup and recovery. The password should not contain white space characters. The VMware user privileges that are required are described in Creating ESX Backup User section below. The user name and password must be the same for the ESX server where the VM is running and VMware vCenter server. The user account must be local to the ESX server (login to ESX server and create the VMware user), not a vCenter-wide/domain account used on the ESX server.
The backup data can be encrypted and/or compressed. The compression and encryption are performed on the Amanda server and can consume significant CPU/memory resources.
It is a good idea to Disable Staging for VMware DLEs because they do not add any performance for VMware application.
- Please resolve any configuration errors found by the ZMC Backup What page.
- Change the Data Not Sent Timeout value in the Backup How page for the backup set. The value should be increased to at least 7200 seconds. Increasing the value does not impact the backup window (time to complete the backup).
Scheduling backups of VMware Server
You can schedule backups using Zmanda Management Console Backup When page or run immediate backups for the backup set from the Backup Activate page.
The status of the backup are shown in the Monitor page. Backup reports will be available under the Report tab in the Zmanda Management Console.
The backups of the guest VM are performed by taking snapshots of the disks associated with the guest VMs. Snapshots are removed after the backup data is copied over. Under certain circumstances, the snapshots are not removed. It is important to remove the backup snapshots.
Performing VMware Server Restores using ZMC
Zmanda Management Console can restore the VM directly to another or the original ESX server.
The ZMC recovery process starts at Restore What page. Enter the Backup Date - the timestamp of the backup run. The Host Name in case of VMware is always 127.0.0.1. Enter the Alias/Directory/Path (guest VM name) in \\<esx or vCenter server name>\<datastore name>\<guest VM name> format. It should be exactly same as what was entered in ZMC Backup What page.
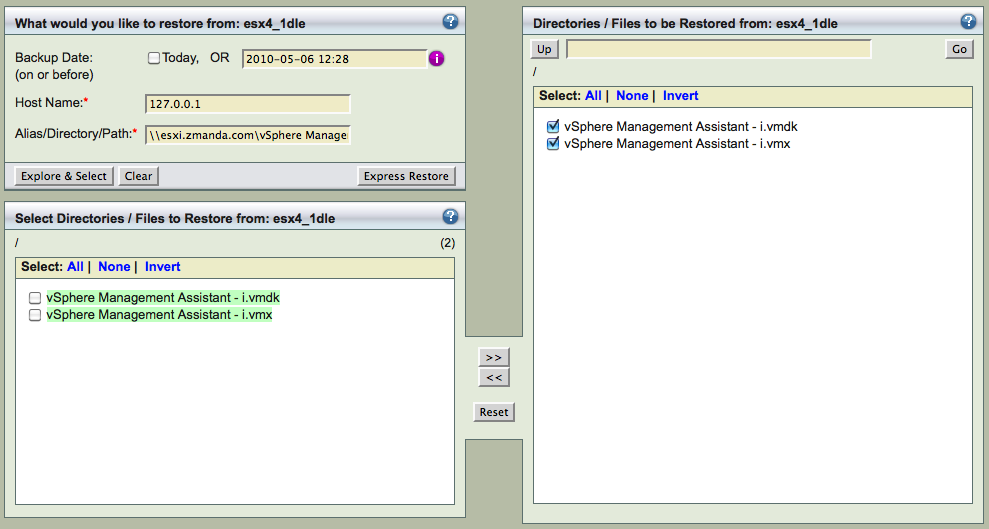
In the Restore Where page, Select Destination Host as localhost. The Destination Directory can be one of the following:
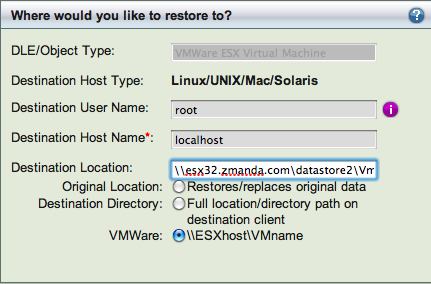
- Original Location: Backup to the original ESX server with the same guest VM name. Please make sure the guest VM no longer exists on the original ESX server. Guest VM backed up using VMware vCenter cannot be restored to original ESX server.
- Destination Directory: A directory on the Amanda server which sufficient space to store restored images. Only level 0 backups (full backups) can be restored to the Amanda server directory. Level 1 backups contain only changed data blocks and cannot be applied without VMware. Example: /vmware-restore
- VMware: The VM to be restored to should be specified in format //<esx server name>/<datastore name to restore to>/<guest vm name> if the VM has to be restored to the ESX server and started on the ESX server. The guest VM name and ESX server can be different from the original VM name and the ESX server. You cannot restore to the original VM name unless it is removed from the inventory. The guest VM name can only have a-zA-Z_- characters. You cannot use VMware vCenter name and a specific ESX server must be provided.
If you are restoring to an alternate ESX server (not the original ESX server from where backup was performed), the /etc/amanda/<backupset name>/esxpass file should contain ESX user name and password for the ESX server being restored to.
An example esxpass file is shown below:
//esx4.company.com root%root_password
esx4.company.com is the IP address or the name of the ESX server. root is the user on the ESX server used for the backup and restore operations and password for the user is root_password. The password must not be encrypted.
After reviewing the entries, Click Restore button on the Restore Restore page to start the restore process as shown below:
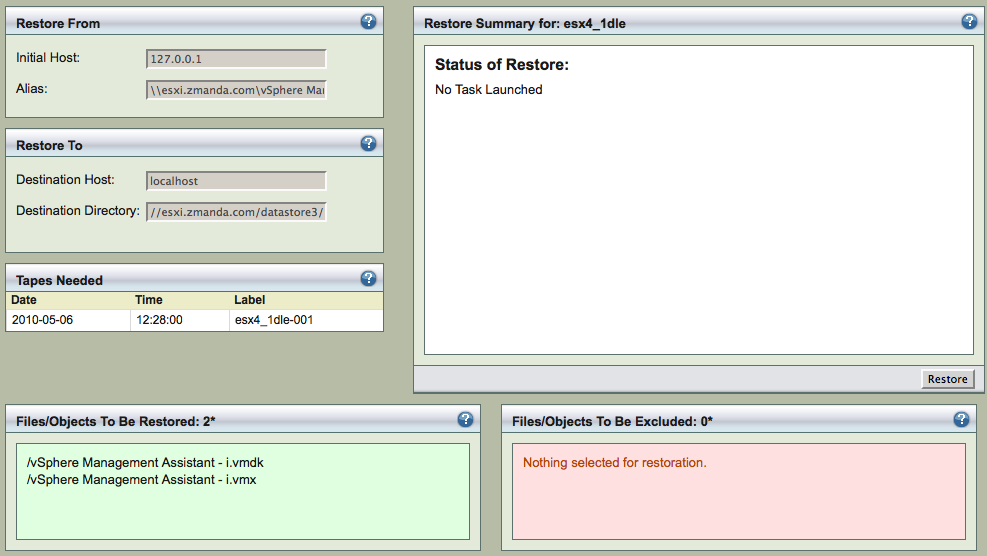
When errors occur, the temporary space used for restoration (Destination Directory) is not cleaned up after restoration. This should be done manually.
The CDROM device file name on the restored VM may not be correct. It should be verified on the restored VM.
Please log in to ESX server to see the restored folder and to troubleshoot restore issues. You may not be able to see the restored datastores from the vCenter server.
Performing VMware Server Restores/Recovery using command line
This section describes how to use Amanda recovery command amrecover to perform ESX guest VM recovery. This procedure can be used to restore guest VM to the original ESX server. These steps can be used instead of the procedure described in the previous section.
- Run amrecover command on the Amanda server as root user. You will need to provide the backup set name as a parameter. The values for options -t and -s will not change.
# amrecover -C <backup set name> -t localhost -s localhost
- Set the host to localhost and the disk to DLE name that was used in the backup set configuration. The DLE name will have //<ESX server name>/<name of the guest VM>. The setdisk parameter must match the name (include escape characters) that was specified in the disklist.conf configuration file.
amrecover> sethost localhost
200 Dump host set to localhost.
amrecover> setdisk //192.168.1.2/rhel4-32
200 Disk set to //192.168.1.2/rhel4-32
- To restore the VM to a different ESX server or to different VM name, user setproperty sub-command. If this property is not specified, the VM will be restored to original ESX server and original VM name.
amrecover> setproperty directory //192.168.1.3/datastore2/amanda-restore/amanda-orig/backupsetname
The syntax of directory value is //restore-esxi/datastore/target-name/orig-name/backupsetname
- You list the files in the backup using ls command. Add all the files to be restored and run extract command to restore the files.
amrecover> ls
2010-03-03-17-22-35 rhel4-32.vmx
2010-03-03-17-22-35 rhel4-32.vmdk
2010-03-03-17-22-35 .
amrecover> add *
Added file /rhel4-32.vmx
Added file /rhel4-32.vmdk
amrecover> extract
- The VMDKs will be restored to the ESX server and the datastore.
Creating ESX User for Amanda backups
For VMware backup and restore operations, the ESX user that is specified in the ZMC Backup What page should have certain roles. These are minimum set of privileges required for the user. The privileges required for backup are:
[Datastore]
Allocate space
Browse datastore
Low level file operations
[Virtual machine]
[Configuration]
Disk change tracking
Disk lease
[Provisioning]
Allow read-only disk access
Allow virtual machine download
[State]
Create snapshot
Remove snapshot
Rename snapshot
The privileges required for restoration are:
[Datastore]
Allocate space
Browse datastore
Low level file operations
Update virtual machine files
[Network]
Assign Network
[Resource]
Assign virtual machine to resource pool
[Virtual Machine]
[Configuration]
Add new disk
Add or remove device
Advanced
Change resource
Disk change tracking
Disk lease
Host USB Device
Modify device settings
Settings
[Inventory]
Create New
Register
[Provisioning]
Allow disk access
Allow virtual machine files upload
Please note that the ESX user should have administrator role on the whole ESX server not just the specific Virtual Machines being backed up.
- Select View > Administration > Roles
- Select Add Role. Select an unique name for the role. For example: backup-role
- Select the list of privileges for this role as shown below and click OK to save the role configuration.
.png)
After creating the role, assign the role to specific user that can be used for VMware backups.
- Using VMware Vsphere Client, Log in to the ESX server.
- Select the host in the inventory and click on the Permissions tab.
- Select the user name and use the right-click menu to select Properties.
- Assign the backup role to this user.
